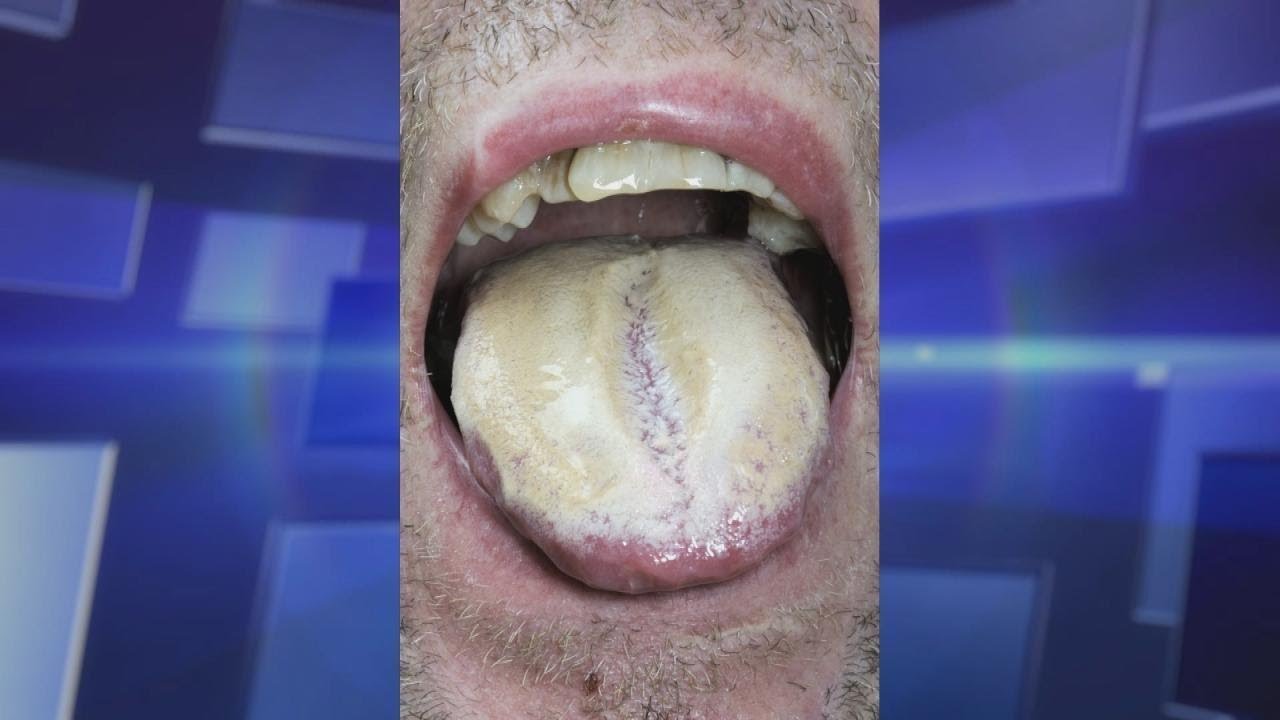
If you find yourself taking amoxicillin and experiencing discomfort in your mouth, it’s important to consider the possibility of oral thrush. This condition arises when there is an overgrowth of Candida yeast, often triggered by antibiotics like amoxicillin that disrupt the normal balance of bacteria in your mouth. Recognizing the signs early can help you take action swiftly.
Symptoms of oral thrush include white patches on your tongue and inside your cheeks, redness, and soreness. You might also notice difficulty swallowing or a cotton-like feeling in your mouth. If these symptoms surface, consult your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
To prevent oral thrush while on amoxicillin, maintain good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, and consider using an antifungal mouthwash as suggested by your healthcare provider. Staying hydrated and eating yogurt with live cultures can also support the restoration of healthy oral flora during antibiotic treatment.
Addressing oral thrush quickly is key. Treatment options typically include antifungal medications, which can alleviate symptoms and restore balance. Monitor your health and seek guidance from a professional if you suspect you have oral thrush after taking amoxicillin.
- Oral Thrush from Amoxicillin
- Prevention Strategies
- Treatment Options
- Understanding Oral Thrush and Its Causes
- The Link Between Amoxicillin and Fungal Infections
- Understanding Fungal Growth
- Prevention and Management Strategies
- Symptoms of Oral Thrush Induced by Amoxicillin
- Preventing Oral Thrush While Taking Amoxicillin
- Treatment Options for Oral Thrush Related to Antibiotics
- When to Seek Medical Advice for Oral Thrush
- Signs That Require Attention
- Risk Factors to Consider
Oral Thrush from Amoxicillin
Take proactive steps if you notice signs of oral thrush after using amoxicillin. This antibiotic can disrupt the balance of bacteria in your mouth, leading to an overgrowth of yeast. Look for symptoms such as white patches on the tongue or inside the cheeks, soreness, or difficulty swallowing.
Prevention Strategies
While on amoxicillin, maintain good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and consider using an antimicrobial mouthwash. Staying hydrated supports your immune system, which helps reduce the risk of yeast overgrowth. Eating yogurt with live cultures may also restore beneficial bacteria in your mouth and gut.
Treatment Options
If you develop oral thrush, consult your healthcare provider for treatment options. Antifungal medications, such as nystatin or fluconazole, can effectively eliminate the yeast. Additionally, adjusting your antibiotic regimen might be necessary if thrush becomes a recurrent issue. Regular follow-ups will help monitor your condition and guide appropriate interventions.
Understanding Oral Thrush and Its Causes
Oral thrush, caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast, occurs when the balance of microorganisms in the mouth is disrupted. This condition manifests as white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and roof of the mouth. To prevent oral thrush, proper oral hygiene is crucial. Regular brushing and flossing help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria and yeast.
Antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, can disrupt this balance by killing beneficial bacteria that normally keep Candida in check. Extended use of these medications increases the risk of developing oral thrush. If you must take antibiotics, consider using probiotic supplements to help restore healthy bacteria in the mouth and gut.
Other factors contributing to oral thrush include a weakened immune system, diabetes, and dry mouth. Individuals with certain medical conditions or those undergoing specific treatments should monitor their oral health closely. Maintaining hydration can help prevent dry mouth, reducing the risk of yeast overgrowth.
If you experience symptoms of oral thrush, consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment options. Antifungal medications can effectively treat the condition, but addressing the underlying causes is equally important to prevent recurrence.
The Link Between Amoxicillin and Fungal Infections
Amoxicillin can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the body, leading to an increased risk of fungal infections such as oral thrush. This antibiotic effectively targets bacteria but may also eliminate beneficial bacteria that keep fungal populations in check.
Understanding Fungal Growth
The mouth harbors numerous bacteria and fungi, including Candida species. A healthy bacterial environment normally prevents Candida from overgrowing. However, when taking amoxicillin, beneficial bacteria decline, creating an opportunity for fungi to proliferate.
- Candida albicans is the most common fungal species responsible for oral thrush.
- Individuals who are immunocompromised or have underlying health conditions are at greater risk.
Prevention and Management Strategies
To minimize the risk of oral thrush while taking amoxicillin, consider the following strategies:
- Probiotics: Incorporating probiotics can help restore healthy bacterial levels. Yogurt and fermented foods are good sources.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain a strict oral hygiene routine. Brush teeth regularly and consider using an antifungal mouthwash if necessary.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep the mouth moist and wash away excess yeast.
- Limit Sugar Intake: Reducing sugar consumption can decrease the likelihood of fungal growth.
If symptoms of oral thrush appear, such as white patches in the mouth or difficulty swallowing, consult a healthcare provider for an appropriate antifungal treatment. Always discuss any concerns about antibiotics and their side effects with your doctor to determine the best strategy for your health.
Symptoms of Oral Thrush Induced by Amoxicillin
Oral thrush manifests through distinct symptoms that require immediate attention. Look for creamy white lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, and sometimes the roof of the mouth. These lesions can resemble cottage cheese and may bleed slightly if scraped.
Another common symptom is irritation or soreness in the mouth. You might notice a burning sensation, particularly when consuming spicy or acidic foods. A dry mouth also frequently accompanies thrush, leading to discomfort during daily activities like eating and swallowing.
Alterations in taste perception often occur as well. Individuals may find that food tastes different, or they might experience a metallic taste. Bad breath can develop, which may be an additional concern.
If the infection spreads, it might lead to difficulty swallowing or a feeling of something stuck in the throat. In rare cases, fever and systemic symptoms can present, indicating a more severe infection.
Promptly addressing these symptoms with a healthcare provider is crucial for effective management. Early intervention can ease discomfort and prevent further complications.
Preventing Oral Thrush While Taking Amoxicillin
Maintain good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to reduce the risk of fungal growth.
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush. This helps avoid irritation in the mouth and reduces the chance of developing thrush.
Rinse your mouth after taking amoxicillin. Swish with water or a saltwater solution to minimize bacterial buildup.
Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your mouth moist and tooth-friendly.
Incorporate probiotics into your diet. Foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables support a healthy balance of bacteria in the mouth.
- Opt for low-sugar options to limit yeast growth.
- Consider probiotic supplements after discussing with a healthcare provider.
Limit sugary foods and drinks. High sugar intake can promote yeast growth, leading to thrush.
Consult your healthcare provider if you have a history of oral thrush. They may recommend preventive antifungal medications or alternative antibiotics.
Monitor your mouth for early signs of thrush. Spotting symptoms early allows for quicker treatment and minimizes discomfort.
Report any changes in your mouth or health to your healthcare provider promptly. Early intervention can stop thrush from taking hold.
Treatment Options for Oral Thrush Related to Antibiotics
Antifungal medications form the cornerstone of treatment for oral thrush linked to antibiotic use. Nystatin, available as a mouth rinse or lozenge, effectively targets the yeast responsible for candidiasis. Swish the solution in your mouth and swallow it to maximize benefits.
Fluconazole represents another potent option. This oral medication, usually taken in a single dose, can clear the infection effectively. Consult your healthcare provider for the appropriate dosage and duration based on your specific needs.
Probiotic supplementation may aid recovery by restoring balance to oral flora. Look for products containing Lactobacillus species, as they can help outcompete Candida yeast. Incorporate yogurt or fermented foods into your diet for natural sources of probiotics.
Maintain good oral hygiene to prevent recurrence. Brush teeth at least twice daily and floss regularly. Rinse your mouth after meals to reduce sugar and food particles that feed yeast growth.
If you struggle with dry mouth, consider using saliva substitutes or drinking plenty of water. A hydrated mouth can help stave off thrush development.
Finally, monitor your symptoms. If over-the-counter treatments don’t bring relief, consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and potential prescription options. Staying proactive ensures effective management of oral thrush.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Oral Thrush
If you suspect you have oral thrush after taking amoxicillin, consult your healthcare provider if you experience persistent symptoms such as white patches in your mouth, soreness, or difficulty swallowing. Early intervention can prevent complications and promote effective treatment.
Signs That Require Attention
Monitor your symptoms closely. Seek medical advice if you notice:
- White lesions that don’t heal within two weeks
- Painful swallowing or feeling like food is stuck
- Significant redness or swelling in the mouth
- Fever or excessive fatigue
Risk Factors to Consider
If you have underlying health issues such as diabetes, HIV, or weakened immune systems, your risk for complications increases. Consult your healthcare provider for a tailored approach if you’re at risk.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Persistent white lesions | Schedule a doctor’s appointment |
| Pain while swallowing | Contact healthcare provider |
| Severe fatigue | Discuss symptoms with a doctor |
| Other infections | Seek immediate medical help |
Taking proactive steps and consulting a healthcare professional can lead to more effective management of oral thrush. Don’t hesitate to reach out for help when needed.