Start treatment for aplastic anemia with prednisone as a steroid option to address inflammation and immune response. This medication helps in modulating the body’s immune system, which plays a crucial role in this condition. Prednisone is often used as a part of the initial therapy and can lead to significant improvements in blood counts for many patients.
Monitor dosages carefully; healthcare providers typically start with a higher dose, then gradually reduce it based on the patient’s response. Regular blood tests are essential to track changes in blood cell counts, allowing adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. Ensure you understand potential side effects of prednisone, such as weight gain, mood changes, and increased risk of infections.
Support your overall treatment strategy with a balanced diet and adequate rest. Engage with your healthcare team to discuss any concerns about your medication, and ask questions to clarify your understanding of the treatment process. Staying informed and actively participating in your care can significantly enhance your healing journey.
- Aplastic Anemia and Prednisone: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding Aplastic Anemia: Definition and Causes
- Defining Aplastic Anemia
- Causes of Aplastic Anemia
- Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia: Recognizing the Condition
- How Prednisone Works in Treating Aplastic Anemia
- Dosage Guidelines for Prednisone in Aplastic Anemia Treatment
- Initial Dosing
- Adjustments and Monitoring
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone Therapy
- Monitoring Treatment Response: What Patients Should Expect
- Symptoms Tracking
- Follow-Up Appointments
- Alternative Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia
- Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies to Support Treatment
- When to Seek Medical Advice During Prednisone Treatment
- Monitor Mood Changes
- Evaluate Physical Symptoms
Aplastic Anemia and Prednisone: A Comprehensive Overview
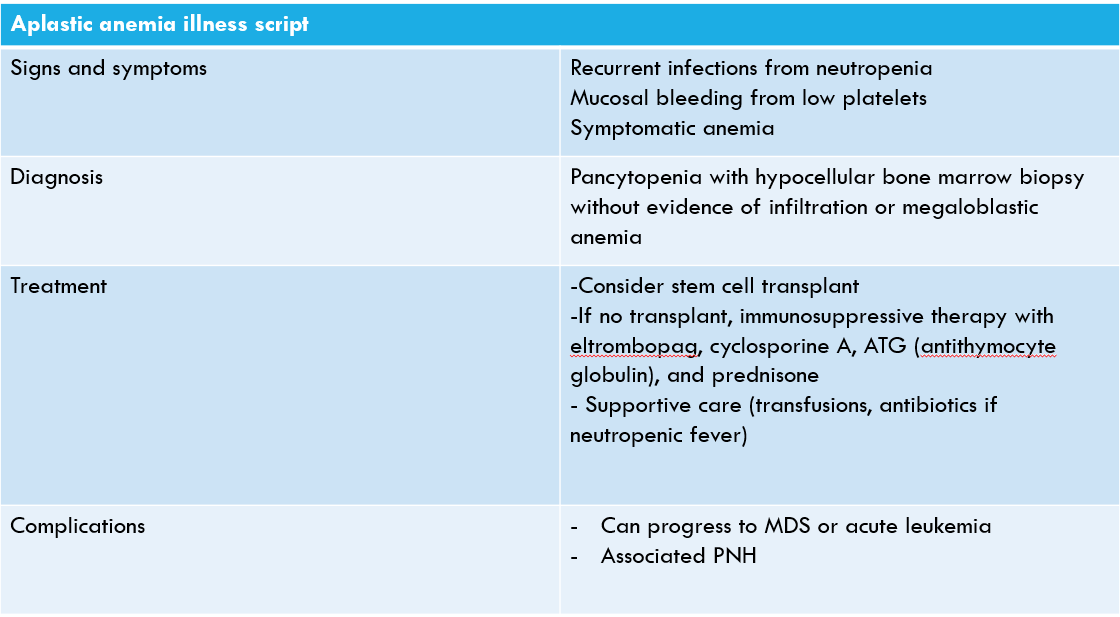
Aplastic anemia treatment often involves the use of prednisone. This medication reduces inflammation and modulates the immune response, which can help in managing symptoms associated with this condition. Prednisone is particularly beneficial when aplastic anemia is due to an autoimmune reaction.
While prednisone offers advantages, monitoring for side effects is essential. Patients may experience weight gain, increased appetite, mood changes, or gastrointestinal issues. Discuss these potential side effects with a healthcare provider to manage them effectively.
Regular blood tests are crucial to evaluate treatment response and adjust dosages as needed. These tests help track blood cell counts and ensure that the body is responding adequately to the treatment.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Dosage | Typically starts at a higher dosage, then tapered based on response and side effects. |
| Administration | May be taken orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the condition. |
| Monitoring | Regular monitoring of blood counts is necessary to assess effectiveness. |
| Duration | Treatment duration varies, often requiring long-term management. |
| Combined Therapy | May be used alongside other medications like antithymocyte globulin (ATG) or cyclosporine. |
Consultation with a hematologist is advisable for those diagnosed with aplastic anemia. This specialist can provide tailored treatment plans that may include prednisone, in combination with other therapies, based on individual patient needs.
Understanding the management of aplastic anemia with prednisone empowers patients to engage actively in their treatment. Stay informed and participate in discussions about your health to optimize outcomes.
Understanding Aplastic Anemia: Definition and Causes
Aplastic anemia occurs when the bone marrow fails to produce sufficient blood cells. This leads to a deficiency of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, significantly impacting the body’s ability to function normally.
Defining Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is categorized as a form of bone marrow failure. It can be either acquired or inherited. In acquired aplastic anemia, bone marrow damage occurs due to various factors, whereas inherited types arise from genetic defects. The condition can lead to severe fatigue, increased risk of infections, and excessive bleeding.
Causes of Aplastic Anemia
Understanding the causes helps in identifying potential risks and management strategies. The primary causes include:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus can cause the immune system to attack bone marrow.
- Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Chemicals such as benzene and certain pesticides can lead to marrow damage.
- Medications: Some drugs, particularly those used for chemotherapy, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory medications, can contribute to bone marrow suppression.
- Viral Infections: Viruses like hepatitis, Epstein-Barr, and HIV may disrupt the bone marrow function.
- Radiation Exposure: High levels of radiation can harm bone marrow, increasing the risk of aplastic anemia.
- Genetic Conditions: Disorders such as Fanconi anemia or dyskeratosis congenita can predispose individuals to developing aplastic anemia.
Recognizing these causes enables targeted approaches for prevention and treatment. Regular medical check-ups can aid in early detection and management of potential risk factors.
Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia: Recognizing the Condition
Monitor your health closely for signs of aplastic anemia. Key symptoms include fatigue, which often manifests as persistent tiredness unrelated to activity levels. Pay attention to unusual bruising or bleeding, such as frequent nosebleeds or heavy menstrual periods.
Signs of anemia like pale skin or shortness of breath during daily activities indicate reduced red blood cell counts. Additionally, elevated heart rates can signal that your body is struggling to deliver enough oxygen. Observe any increased susceptibility to infections, which stems from low white blood cell counts.
Detecting these symptoms early can help prompt a discussion with your healthcare provider. Regular blood tests can confirm diagnoses and monitor your condition effectively. Make note of any concerning changes and discuss them with a medical professional for timely intervention.
How Prednisone Works in Treating Aplastic Anemia
Prednisone acts as an immunosuppressant, reducing inflammation and modulating the immune response. In cases of aplastic anemia, where the bone marrow fails to produce sufficient blood cells, prednisone helps to counteract the immune system’s attack on the marrow. By dampening this immune response, it allows the bone marrow to recover and regenerate blood cell production.
This medication influences various pathways within the immune system. It interferes with the function of lymphocytes, particularly T-cells, which are often responsible for the destruction of hematopoietic stem cells in aplastic anemia patients. Lowering the activity of these cells promotes an environment conducive for hematopoiesis, the process by which blood cells are formed.
Additionally, prednisone enhances the production of certain proteins that further reduce inflammation. This can lead to a decrease in the cytokines that contribute to the autoimmune aspect of aplastic anemia. With reduced cytokine levels, the process of blood cell formation in the bone marrow can proceed more effectively.
Monitoring is key when using prednisone. Regular blood tests help assess the response to treatment and adjust dosages to minimize side effects. Patients may experience changes in weight, mood, and blood sugar levels. It’s important to communicate any concerns with a healthcare provider to ensure the treatment remains conducive to recovery.
By strategically using prednisone, healthcare providers aim to stabilize the patient’s condition and enhance the bone marrow’s functionality, ultimately supporting the restoration of normal blood counts.
Dosage Guidelines for Prednisone in Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Prednisone dosage starts typically from 1 to 2 mg/kg/day. Adjust based on the patient’s weight, overall condition, and response to treatment. Short-term therapy may require higher doses, while maintenance doses generally range from 5 to 10 mg/day.
Initial Dosing
- Begin with 1-2 mg/kg/day for adults.
- For pediatric patients, start at 2 mg/kg/day, not to exceed 60 mg/day.
- Monitor for side effects and therapeutic response within the first week.
Adjustments and Monitoring
- Reduce dosage gradually upon improvement, aiming for the lowest effective dose.
- Reassess weekly to determine if further adjustments are needed.
- If significant side effects occur, consider temporary or permanent dosage reduction.
Regular blood tests help monitor blood counts and assess treatment efficacy. Encourage patients to report any adverse reactions promptly. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice tailored to individual needs.
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone Therapy
Prednisone therapy can lead to several side effects. Weight gain commonly occurs due to increased appetite and fluid retention. Monitor your dietary habits to minimize this effect. Adjusting your meal plan to include more fruits and vegetables can help manage weight.
Another frequent issue is mood changes. Some patients experience anxiety, irritability, or mood swings. Regular communication with your healthcare provider about these feelings is vital. They may suggest support strategies or adjustments to your treatment plan.
Bone density can decrease with long-term prednisone use. Incorporate weight-bearing exercises and ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D. Discuss the need for bone density screenings with your physician.
Increased risk of infections is another concern due to immune system suppression. Practice good hygiene and avoid close contact with sick individuals. Keep up with vaccinations as recommended by your doctor.
Gastrointestinal issues like stomach ulcers may arise. Taking prednisone with food can mitigate this risk. If you notice symptoms like abdominal pain or persistent nausea, contact your healthcare provider.
Long-term use can also impact blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring may be necessary, particularly if you have diabetes. Discuss potential adjustments to your diabetes management plan with your healthcare team.
Skin changes, such as thinning and easy bruising, can occur. Gentle skin care routines and sun protection are advisable. Inform your doctor if you notice significant changes in your skin’s condition.
Be proactive about managing these side effects through lifestyle changes and regular check-ups. Open dialogue with your healthcare provider ensures that any issues are addressed promptly, allowing you to maintain your quality of life while receiving treatment.
Monitoring Treatment Response: What Patients Should Expect
Regular blood tests are fundamental for assessing your response to prednisone in treating aplastic anemia. Expect to have complete blood counts (CBC) performed frequently, typically every few weeks, to monitor levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This helps your healthcare provider determine the effectiveness of the treatment and make necessary adjustments.
Symptoms Tracking
Pay close attention to how you feel during treatment. Report any changes in symptoms, such as fatigue, dizziness, or signs of infection. Communicating these observations helps your doctor gauge your treatment response and adjust the plan if needed.
Follow-Up Appointments
Keep all follow-up appointments with your healthcare team. They will evaluate lab results and physical symptoms to assess your progress. These visits also offer an opportunity to discuss any side effects from prednisone and how to manage them. Your active participation is key to achieving the best outcomes.
Ultimately, being proactive in monitoring your health and communicating with your healthcare provider can significantly enhance your treatment experience.
Alternative Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia
Consider immunosuppressive therapy (IST) as an initial approach if you are not a candidate for a stem cell transplant. Medications like antithymocyte globulin (ATG) and cyclosporine are commonly used. They help reduce the immune response, allowing the bone marrow to recover.
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) might be beneficial to prevent infections, especially in patients with low platelet counts. This treatment can boost immunity temporarily, aiding in infection control.
Evaluating the role of androgens, such as danazol, can also be worthwhile. These hormones stimulate red blood cell production and can improve blood counts in some patients.
Consider blood transfusions to manage severe anemia and thrombocytopenia. Regular transfusions provide immediate relief and support while other treatments take effect.
Platelet growth factors, like eltrombopag, may be beneficial for patients with low platelet counts. They promote the production of platelets in the bone marrow, reducing the risk of bleeding.
Participation in clinical trials offers access to new therapies. Investigational drugs are often evaluated and could present additional treatment options tailored to your needs.
Nutritional support plays a significant role in recovery. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals aids overall health and can support treatment outcomes. Focus on foods high in folate and iron for optimal blood cell production.
Integrative approaches, including acupuncture and herbal supplements, may help manage symptoms such as fatigue and stress. Consult healthcare professionals before starting any alternative therapies.
Regular follow-ups with a hematologist ensure appropriate monitoring and adjustments to your treatment plan. Staying updated on the latest research offers the best chance for successful management of aplastic anemia.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies to Support Treatment
Maintain a balanced diet rich in iron and vitamin B12 to enhance your blood health. Incorporate foods like leafy greens, legumes, nuts, and lean meats. Regularly include citrus fruits to boost vitamin C intake, which aids iron absorption.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Proper hydration supports overall health and can help your body function better during treatment.
Engage in gentle physical activity, such as walking or yoga, to improve circulation and reduce fatigue. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week, adjusting intensity based on your energy levels.
Prioritize quality sleep by establishing a regular sleep schedule. Create a calming bedtime routine and ensure your sleep environment is comfortable and dark to enhance restfulness.
Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness. Allocate time for hobbies and activities that bring joy and relaxation, which can positively impact your mindset and overall well-being.
Limit exposure to infections by practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding crowded places. Stay up-to-date with vaccinations as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Consult a nutritionist for personalized dietary guidance and to address any specific deficiencies related to your treatment. They can provide tailored advice to help optimize your nutrition.
Incorporate herbal supplements like ashwagandha or ginseng only after discussing them with your healthcare provider, as some herbs may interact with medications.
Build a supportive network of family and friends. Sharing experiences and feelings with loved ones can alleviate emotional stress and align you with a community that understands your journey.
Consider joining a support group for individuals with aplastic anemia. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can offer valuable insights and emotional support.
When to Seek Medical Advice During Prednisone Treatment
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience any severe or unusual side effects while taking prednisone. Symptoms such as significant weight gain, swelling, or persistent high blood pressure warrant attention. Pay close attention to signs of infection, including fever, chills, or a persistent sore throat, as prednisone can weaken your immune response.
Monitor Mood Changes
Report any drastic mood changes or signs of depression. Prednisone may cause psychological effects, and it’s important to seek help if you feel anxious or irritable. Additionally, if you notice insomnia or unusual cravings, these may indicate the need to adjust your treatment plan.
Evaluate Physical Symptoms
Stay alert for gastrointestinal issues like severe abdominal pain, persistent nausea, or vomiting, which may signal complications. If you develop skin rashes, bruising easily, or other skin changes, reach out to your doctor for guidance. Regular check-ups are recommended to monitor your blood counts and ensure overall health.