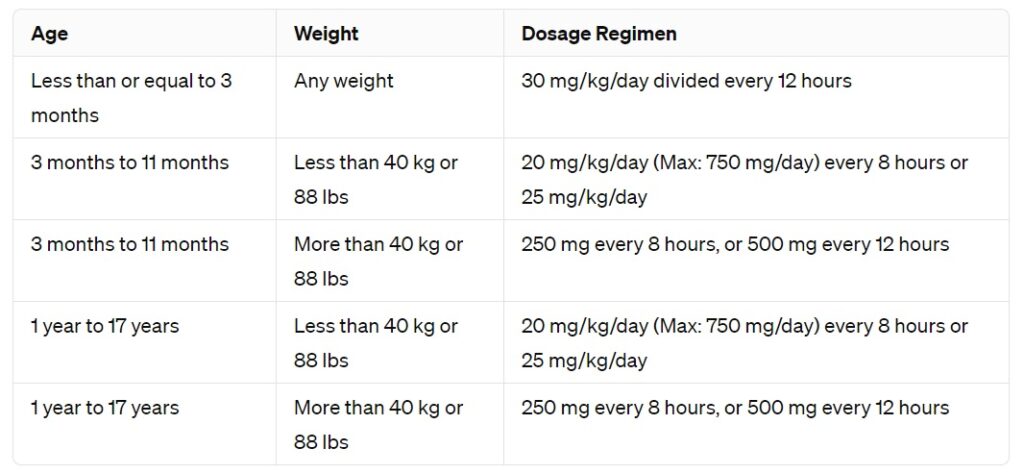
For optimal treatment outcomes, administer Amoxicillin at a dosage of 20 to 40 mg/kg per day, divided into two or three doses, depending on the severity of the infection. Always consider the patient’s age, weight, and specific health conditions when determining the appropriate dosage.
When treating mild to moderate infections, such as respiratory or urinary tract infections, a dosage closer to the lower end of this range is typically sufficient. In more serious situations, increase the dosage to the upper limit to enhance the drug’s efficacy and combat the infection more aggressively.
To ensure accuracy in dosing, utilize precise measurements of the patient’s weight. For children, calculate the dosage based on their weight in kilograms rather than general age guidelines, allowing for a more tailored and safe treatment approach. Always monitor for any adverse reactions, as individual responses can vary widely.
Understanding Amoxicillin Dosage in mg/kg
The recommended dosage of Amoxicillin for children typically ranges from 20 to 40 mg/kg per day, divided into two or three doses. For mild to moderate infections, 20 mg/kg is often effective, whereas more severe infections may require up to 40 mg/kg. Dosage adjustments depend on the type and severity of the infection, the patient’s age, and kidney function.
Calculating Dosage
To calculate the appropriate dose, first determine the child’s weight in kilograms. Multiply this weight by the recommended range of 20 to 40 mg/kg. For example, a child weighing 25 kg would require between 500 mg (25 kg x 20 mg) and 1000 mg (25 kg x 40 mg) of Amoxicillin per day, depending on their condition.
Administration Tips
Administer Amoxicillin orally, with or without food. Ensure doses are spaced evenly throughout the day to maintain effective blood levels. Monitor for any side effects, such as nausea or allergic reactions, and contact a healthcare provider promptly if any severe symptoms arise. Following dosage recommendations helps ensure effective treatment and minimizes the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Calculating Amoxicillin Dosage for Pediatric Patients
For pediatric patients, the recommended dosage of Amoxicillin typically ranges from 20 to 40 mg/kg/day, divided into two or three doses. For mild to moderate infections, administer 20 mg/kg/day, while for more severe infections, adjust the dosage to 40 mg/kg/day. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 1,000 mg.
Calculating the Dose
To calculate the dosage, first determine the weight of the child in kilograms. Multiply the child’s weight by the desired dose (20 or 40 mg). For example, for a child weighing 15 kg and requiring a dosage of 30 mg/kg/day, the calculation would be 15 kg x 30 mg = 450 mg per day. This can then be divided into two or three doses, such as 225 mg every 12 hours.
Adjustments and Considerations
Adjust the dosage in patients with renal impairment. Consult dosing guidelines to determine the appropriate dose based on the patient’s kidney function. Always ensure the total dose remains within safe limits and monitor the patient for potential side effects, such as allergic reactions or gastrointestinal discomfort. This attention to detail helps in achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Factors Influencing Amoxicillin Dosage Calculations
Body weight significantly influences amoxicillin dosing. For pediatric patients, a common calculation is 20-40 mg/kg/day, adjusted for the severity of the infection. Weight must be accurately assessed to ensure effective treatment.
Renal function also plays a crucial role in determining the dosage. In cases of renal impairment, clinicians often reduce the dose or extend the dosing interval to prevent drug accumulation and potential toxicity. Regular monitoring of renal function tests helps tailor the dosage accordingly.
Age and maturity affect drug metabolism. Neonates and infants metabolize medications differently than older children and adults, often requiring specific adjustments to avoid underdosing or overdosing.
The type of infection may necessitate a higher or lower dosage. Some bacterial infections, such as pneumonia, may require larger doses than urinary tract infections. Healthcare providers assess the specific bacteria’s susceptibility and the infection’s severity when calculating dosages.
Patient adherence to the dosing schedule also influences outcomes. Simplifying the regimen can enhance compliance. Prescribing a twice-daily dosing schedule instead of multiple doses throughout the day may improve adherence.
Lastly, concomitant medications might impact amoxicillin’s effectiveness. Certain drugs can alter gut flora or compete for metabolic pathways, requiring careful consideration when calculating individual dosages.