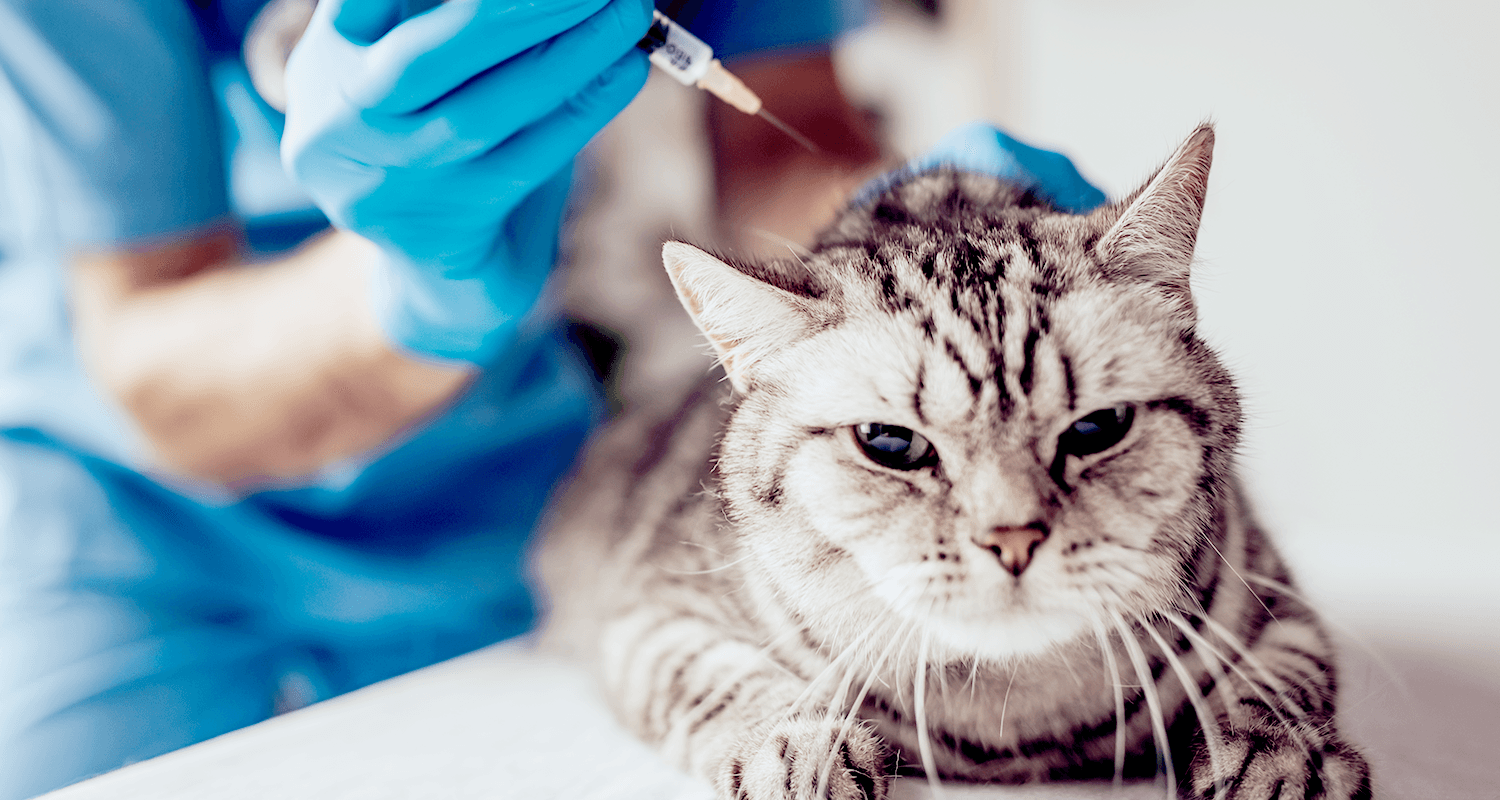
If your cat suffers from inflammation or autoimmune disorders, consider the benefits of prednisone injections as a treatment option. Prednisone is a corticosteroid that helps reduce swelling and effectively manage various conditions in felines. Understanding how to properly administer and monitor the effects of this medication can significantly improve your pet’s quality of life.
Before starting treatment, consult your veterinarian to assess your cat’s specific health needs. Dosage varies based on the underlying condition, so professional guidance ensures that your cat receives the correct amount. Administering the injection under veterinary supervision during the initial treatments allows for prompt observation of any side effects.
Regular follow-ups are critical to adjust the medication as needed. Be vigilant for signs of side effects, such as increased thirst or urination, and report these to your vet. With careful management, prednisone injections can be a powerful tool in addressing your cat’s health challenges.
- Prednisone Injection for Cats
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects and Monitoring
- What is Prednisone and How Does it Work in Cats?
- Mechanism of Action
- Common Uses in Feline Healthcare
- Common Conditions Treated with Prednisone Injections in Cats
- Dosage Guidelines for Prednisone Injection in Cats
- Potential Side Effects of Prednisone Injections in Cats
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Behavioral Changes
- How to Administer Prednisone Injections to Your Cat
- Monitoring Your Cat’s Response to Prednisone Treatment
- Alternatives to Prednisone for Cat Health Management
- Important Considerations Before Starting Prednisone Treatment
- When to Contact Your Veterinarian About Prednisone Use
Prednisone Injection for Cats
Administering a prednisone injection to your cat can effectively manage various health conditions. This corticosteroid reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune response, benefiting cats suffering from allergies, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage depends on the cat’s condition and weight. A veterinarian assesses the specific needs of your pet, often starting with a higher dose that gradually decreases. Administer the injection subcutaneously or intramuscularly, following the vet’s guidelines precisely to ensure optimal results.
Side Effects and Monitoring
Monitor your cat for any side effects such as increased thirst, appetite, or urination. These symptoms are common but report any severe reactions like vomiting or behavior changes to your veterinarian immediately. Regular follow-ups are key to adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
What is Prednisone and How Does it Work in Cats?
Prednisone is a corticosteroid widely used to treat various health issues in cats, including allergies, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory conditions. This medication mimics the effects of hormones produced by the adrenal glands, particularly cortisol, helping to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune response.
Mechanism of Action
When administered, prednisone undergoes conversion into prednisolone, its active form. It works by:
- Suppressing the immune system to reduce inflammation.
- Inhibiting the production of inflammatory substances in the body.
- Increasing the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory proteins.
This results in decreased swelling, redness, and pain, improving the overall comfort and quality of life for the affected cat.
Common Uses in Feline Healthcare
Your veterinarian may prescribe prednisone for:
- Severe allergic reactions or skin conditions.
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus or pemphigus.
- Respiratory issues such as asthma.
- Certain types of cancer to reduce symptoms and improve appetite.
While effective, it’s vital to follow your vet’s dosage instructions closely. Prednisone can cause side effects, especially with long-term use, including increased thirst, appetite changes, and potential weakening of the immune system. Regular veterinary check-ups can help monitor your cat’s response to treatment and adjust as necessary.
Common Conditions Treated with Prednisone Injections in Cats
Prednisone injections effectively manage various health conditions in cats. Here are some common issues addressed by this treatment:
- Allergic Reactions: Prednisone helps control allergic responses caused by food, insect bites, or environmental factors. It reduces inflammation and itching.
- Asthma: For cats suffering from asthma, prednisone can alleviate airway inflammation, improving breathing and overall comfort.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like hemolytic anemia and lupus require immunosuppressive therapy. Prednisone effectively moderates the immune response.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Injections of prednisone reduce intestinal inflammation, promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: While it doesn’t treat the disease directly, prednisone can manage concurrent symptoms like inflammation and nausea.
- Cancer Treatment: In cases of lymphoma or other malignancies, prednisone can reduce tumor size and relieve associated symptoms, contributing to a better quality of life.
Always consult with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment for your cat’s specific health needs. Regular follow-ups help monitor the response to therapy and adjust the treatment plan as necessary.
Dosage Guidelines for Prednisone Injection in Cats
Administering prednisone injections to cats requires careful attention to dosage. Typically, the initial dose ranges between 1 to 2 mg per kilogram of the cat’s body weight. This dosage can be adjusted based on the cat’s response to treatment and any specific medical considerations.
For precise administration, it’s important to follow these steps:
| Weight (kg) | Recommended Dose (mg) | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2-4 | Once daily |
| 4 | 4-8 | Once daily |
| 6 | 6-12 | Once daily |
| 8 | 8-16 | Once daily |
After the initial treatment phase, tapering the dosage is often necessary. Gradually reduce the dose to minimize side effects and allow the body’s natural cortisols to resume production. Always reassess the cat’s condition and consult with a veterinarian to adjust the dosage accordingly.
Monitor for any signs of adverse reactions, such as increased thirst, urination, or changes in appetite. If noticeable side effects occur, contact a veterinarian for advice on potential dosage adjustments or alternative treatments.
Keep detailed records of the cat’s response to the treatment and any side effects to ensure a tailored and safe approach to managing their health with prednisone injections.
Potential Side Effects of Prednisone Injections in Cats
Monitor your cat closely after administering prednisone injections. Common side effects include increased thirst and urination, which may lead to dehydration if not managed properly. Maintain a fresh supply of water and encourage your cat to drink regularly.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Be aware of potential gastrointestinal side effects, such as vomiting or diarrhea. If these occur, consult your veterinarian for advice on how to alleviate discomfort and whether adjustments to the dosage are necessary.
Behavioral Changes
Watch for changes in behavior, including increased aggression or anxiety. Some cats may become more vocal or restless. Address any concerning behavior by discussing it with your veterinarian, who may provide strategies to help your cat adjust.
Long-term use can lead to more serious side effects like weight gain or muscle loss. Regular check-ups with your veterinarian will help monitor your cat’s overall health and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
How to Administer Prednisone Injections to Your Cat
Hold your cat securely in your lap or on a stable surface. It’s key to keep your pet calm during the process. If necessary, enlist someone to gently hold your cat or wrap them in a towel to prevent sudden movements.
Gather all supplies: the prednisone injection, a clean syringe, alcohol swabs, and treats. Ensure that the injection site is clean. Use an alcohol swab to wipe the area on your cat’s skin where you plan to inject.
Without removing the cap, check the syringe for air bubbles. If present, gently tap the syringe and push the plunger slightly to release any air. Once ready, remove the cap and hold the syringe like a pencil.
Choose the injection site, typically the loose skin around the scruff of the neck or the side of the body. Pinch the skin to create a tent, then insert the needle quickly and confidently at a 45-degree angle.
Push the plunger slowly to administer the medication. Once complete, withdraw the needle quickly and apply light pressure to the injection site with a clean cotton ball or gauze to minimize bleeding.
Offer your cat a treat or gentle praise immediately after the injection. This positive reinforcement will help them associate the experience with something pleasant. Always monitor your cat for any adverse reactions after the injection, and consult your veterinarian if concerns arise.
Monitoring Your Cat’s Response to Prednisone Treatment
Keep a close eye on your cat’s behavior and physical changes after beginning prednisone treatment. Regular assessments will help you identify any side effects or improvements.
- Track Appetite: Note any changes in your cat’s eating habits. Increased hunger is common, but decreased appetite may signal a problem.
- Observe Water Intake: Monitor drinking habits. Prednisone can lead to increased thirst, and you should ensure your cat stays hydrated.
- Watch for Weight Changes: Weigh your cat weekly to catch any sudden weight gain or loss. Report significant changes to your veterinarian.
- Monitor Activity Levels: Pay attention to your cat’s energy levels. An increase in activity or unusual lethargy could indicate a reaction to the medication.
- Check for Behavioral Changes: Look for signs of restlessness, aggression, or anxiety. Such changes may require a discussion with your vet.
Regular vet visits are essential to evaluate your cat’s progress. Share your observations during these appointments to assist in tailoring the treatment plan.
If your cat experiences severe side effects, such as persistent vomiting, difficulty breathing, or extreme lethargy, contact your veterinarian immediately. Prompt action can help manage any complications effectively.
Keep a diary of your cat’s symptoms, food, and water intake, and any side effects. This information will be invaluable for your veterinarian in making informed decisions about your cat’s care.
Alternatives to Prednisone for Cat Health Management
Consider using Omega-3 fatty acids as a natural anti-inflammatory option. These can support joint health and reduce inflammation in conditions like arthritis. Fish oil or algae-based supplements rich in EPA and DHA can be beneficial.
Glucosamine and chondroitin supplements enhance joint function and alleviate pain for senior cats or those with mobility issues. Regular administration can improve quality of life by promoting cartilage health.
Herbal remedies such as curcumin, derived from turmeric, provide anti-inflammatory benefits. Always consult a veterinarian for appropriate dosages to ensure safety for your cat’s health condition.
Homeopathy can also be explored for supportive care in conditions like allergies or skin irritations. Remedies such as Apis mellifica may relieve reactions, while Silicea can assist in skin healing.
Acupuncture is a non-invasive treatment option. It can help with pain management and stimulate healing processes. Many cats find the sessions calming, which further contributes to their well-being.
Dietary adjustments play a significant role in managing health. A balanced, high-quality diet tailored to your cat’s specific needs can strengthen their immune system and reduce the incidence of health issues. Incorporating more protein and fewer carbohydrates often yields positive results.
Probiotics support gut health and enhance overall immune response. These beneficial bacteria can mitigate the effects of stress and illness on your cat’s digestive system, fostering a healthier environment internally.
| Alternative Treatment | Benefits | Recommended Form |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduces inflammation | Fish oil capsules |
| Glucosamine & Chondroitin | Supports joint health | Chewable tablets |
| Curcumin | Anti-inflammatory | Powder or capsules |
| Acupuncture | Pain management | Professional session |
| Probiotics | Improves gut health | Powder or capsules |
Evaluate these alternatives with your veterinarian’s guidance. Tailoring the approach to your cat’s specific health needs will ensure the best outcomes for their care.
Important Considerations Before Starting Prednisone Treatment
Consult your veterinarian to confirm the diagnosis and ensure prednisone is the best option for your cat’s condition. Accurate dosing is critical; follow the vet’s instructions meticulously to avoid complications.
Monitor your cat for changes in behavior, appetite, or weight after starting treatment. Adverse reactions may occur, such as increased thirst or urination. Report any concerning symptoms to your vet promptly.
Be wary of potential drug interactions. Share a complete list of your cat’s medications and supplements with the veterinarian to avoid negative effects.
Avoid sudden discontinuation of prednisone. Gradually tapering the dosage, as advised by your vet, helps prevent withdrawal symptoms and adrenal insufficiency.
Maintain regular check-ups for blood tests and overall health assessments. These allow tracking of your cat’s response to treatment and adjusting doses if necessary.
Consider your cat’s health history, particularly any pre-existing conditions like diabetes or infections, which could influence the treatment plan. Your vet may recommend alternative therapies for those cases.
Finally, be informed about the long-term effects of prednisone, especially if your cat requires extended treatment. Discuss any concerns with your veterinarian to ensure a balanced approach to your cat’s health care.
When to Contact Your Veterinarian About Prednisone Use
If you notice any unusual side effects in your cat after starting prednisone, reach out to your veterinarian immediately. Signs like increased thirst, excessive urination, altered appetite, or behavioral changes warrant prompt attention.
Monitor your cat for symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, or lethargy. These could indicate an adverse reaction and should be discussed with your vet. If your cat shows signs of infection, like fever or unusual discharge, contact your veterinarian without delay.
Adjustments in dosage may be necessary if your cat exhibits significant weight gain or develops skin issues. Regular follow-ups are crucial to ensure the treatment remains safe and beneficial.
Always consult your veterinarian before stopping prednisone. Abrupt cessation can lead to withdrawal symptoms. If you consider changing your cat’s medication or treatment routine, discuss it with your vet for appropriate guidance.
Stay attentive to changes in your cat’s health throughout the treatment. Your proactive communication can help manage potential side effects and ensure your pet’s well-being.