If you notice blood in your stool while taking amoxicillin, seek medical attention immediately. Blood in stool can indicate a serious condition, such as gastrointestinal bleeding or an allergic reaction, and should not be overlooked.
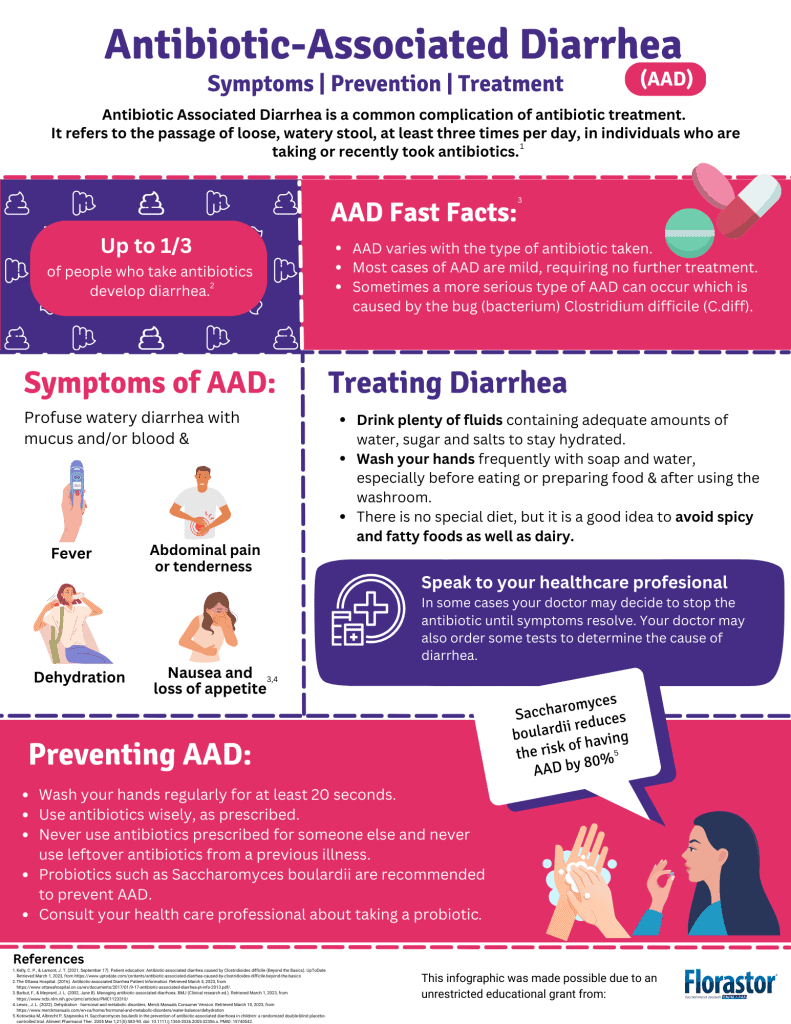
Amoxicillin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic, helps treat various bacterial infections. While it is generally safe, it can cause side effects in some individuals. One of those side effects may include changes in gastrointestinal health. Users often report symptoms like diarrhea, which could be due to Clostridium difficile infection. This bacterial overgrowth can result in inflammation and bleeding in the digestive tract.
Consult your healthcare provider without delay if you experience any gastrointestinal symptoms, especially if accompanied by fever, abdominal pain, or persistent diarrhea. Your doctor may recommend stopping the medication or adjusting your treatment plan to address these issues effectively.
It’s vital to provide your doctor with a comprehensive overview of your health history, including any other medications you’re taking. This information aids in determining if amoxicillin is the right choice for you or if alternative treatments are necessary.
- Amoxicillin and Blood in Stool: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Side Effects
- Common Uses of Amoxicillin
- Possible Side Effects
- Identifying the Causes of Blood in Stool
- The Connection Between Amoxicillin and Gastrointestinal Issues
- What to Do If You Notice Blood in Stool While Taking Amoxicillin
- When to Seek Medical Attention for Blood in Stool
- Associated Symptoms
- Medication Considerations
Amoxicillin and Blood in Stool: A Comprehensive Overview
Consult a healthcare professional immediately if you notice blood in your stool while taking amoxicillin. This symptom can indicate a serious condition that requires prompt attention.
Amoxicillin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic, is generally safe and effective for treating various infections. However, it can disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria, potentially leading to gastrointestinal issues. Such disturbances might result in symptoms like diarrhea, which could vary in severity.
While rare, amoxicillin can trigger Clostridium difficile infection (CDI), characterized by severe diarrhea and possible blood in the stool. CDI occurs when normal gut flora are disrupted. If you experience diarrhea with blood, seek medical evaluation to rule out this complication.
Allergic reactions to amoxicillin may present with gastrointestinal symptoms, including blood-stained stools. Signs of an allergy could include rashes, itching, or swelling. If you suspect an allergic reaction, stop the medication and contact your doctor.
Blood in the stool can stem from other causes unrelated to amoxicillin. Conditions like hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or gastrointestinal bleeding may also lead to similar symptoms. A thorough examination is necessary to identify the exact cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Maintaining a high fluid intake and a balanced diet during antibiotic therapy may help minimize gastrointestinal distress. Probiotics may also restore gut health, but discuss options with your healthcare provider for suitable choices.
Monitor your symptoms closely while on amoxicillin. If unusual signs, such as blood in the stool, develop, timely intervention is key to addressing potential complications swiftly.
Understanding Amoxicillin: Uses and Side Effects
Amoxicillin treats various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and some skin infections. This antibiotic works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, effectively stopping the growth of harmful bacteria. Healthcare providers often prescribe it for conditions such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and ear infections.
Common Uses of Amoxicillin
Doctors commonly recommend amoxicillin for:
- Streptococcal throat infections
- Sinusitis caused by bacteria
- Gonorrhea infections
Possible Side Effects
While many tolerate amoxicillin well, some might experience side effects. These can range from mild to severe. Common side effects include:
| Side Effect | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Nausea | Common |
| Diarrhea | Common |
| Rash | Occasional |
| Allergic reactions | Rare |
In rare cases, serious reactions such as liver dysfunction or severe allergic reactions can occur. Patients who experience symptoms like difficulty breathing or severe stomach cramps should seek medical attention immediately.
Monitor your health closely while taking amoxicillin. Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Identifying the Causes of Blood in Stool
Individuals experiencing blood in stool should seek medical attention immediately. Common causes include hemorrhoids, anal fissures, diverticular disease, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Each condition requires specific treatment strategies.
Hemorrhoids often manifest as bright red blood on the stool’s surface, usually associated with pain during bowel movements. To manage this, consider increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated. Over-the-counter creams can help alleviate discomfort.
Anal fissures, which appear as small tears in the anal canal, can also lead to blood. Symptoms include sharp pain during bowel movements. Applying topical anesthetics and using stool softeners aids in recovery.
Diverticular disease arises from bulging pouches in the intestinal wall. Blood may appear in stool alongside abdominal pain. Treatment often involves antibiotics and dietary adjustments to prevent complications.
Gastrointestinal bleeding can indicate serious conditions, such as ulcers or cancers. This type of blood may be dark or tarry, suggesting a more severe underlying issue. A healthcare provider may perform tests, including endoscopy, to determine the exact cause.
Infections from bacteria or parasites may also result in blood in stool. Prolonged diarrhea, fever, or abdominal cramping warrant immediate health evaluations and possibly lab tests for diagnosis.
Maintaining a symptom diary that tracks food intake, bowel habits, and any accompanying symptoms can provide valuable information to healthcare providers. Early identification of the cause is key to effective treatment and recovery.
The Connection Between Amoxicillin and Gastrointestinal Issues
Amoxicillin can cause gastrointestinal issues in some patients, including diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. These symptoms result from its impact on gut bacteria, potentially leading to an imbalance. It’s vital to monitor gut health during treatment.
In cases where bloody stools occur, immediate medical attention is necessary. This may indicate a serious condition, such as Clostridium difficile infection, particularly after antibiotic use. Patients should report any unexpected symptoms to their healthcare provider promptly.
Probiotics can help restore gut flora balance while taking Amoxicillin. Incorporating probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt or kefir, can support digestive health. Always consult with a healthcare professional before beginning any supplements.
Hydration is essential if gastrointestinal symptoms arise. Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration caused by diarrhea or vomiting. Small, bland meals can also ease discomfort as the digestive system recovers.
Discuss any ongoing or worsening symptoms with a doctor. They may adjust your treatment plan or recommend further diagnostic tests to ensure safety and health. Keeping an open line of communication can lead to better management of medication side effects.
What to Do If You Notice Blood in Stool While Taking Amoxicillin
Immediately contact your healthcare provider if you observe blood in your stool while on amoxicillin. This symptom can indicate a serious side effect or an underlying condition that requires prompt attention.
Follow these steps:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a record of when you first noticed the blood, its appearance, and any accompanying symptoms like pain or diarrhea.
- Avoid Over-the-Counter Remedies: Refrain from taking medications without consulting your doctor, as they might mask symptoms.
- Stay Hydrated: Ensure you drink enough fluids to prevent dehydration, especially if experiencing diarrhea.
- Review Current Medications: Make a list of all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This information will assist your healthcare provider.
- Be Honest: Inform your healthcare provider about any other symptoms, including allergic reactions, rash, or gastrointestinal issues.
In many cases, blood in stool may not directly relate to amoxicillin, but swift communication with your doctor will help determine the cause and necessary actions. Prioritize your health by seeking professional guidance without delay.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Blood in Stool
If you notice blood in your stool, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Blood can indicate various underlying conditions, some of which require immediate care. For example, contact your healthcare provider if the blood appears bright red, suggests a more acute issue, or if you have dark, tarry stools, which may indicate bleeding higher in the digestive tract.
Associated Symptoms
Pay attention to any accompanying symptoms. If you experience severe abdominal pain, dizziness, or fainting, visit the emergency room right away. Significant weight loss or a change in bowel habits alongside blood in the stool also warrants immediate evaluation.
Medication Considerations
If you are taking medications, especially NSAIDs or blood thinners, and notice blood in your stool, consult your healthcare provider as soon as possible. These medications can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, and timely intervention may be necessary.
Never ignore blood in your stool, as it may be a sign of a serious health condition. Schedule an appointment with your doctor or go to the nearest healthcare facility to ensure your well-being.