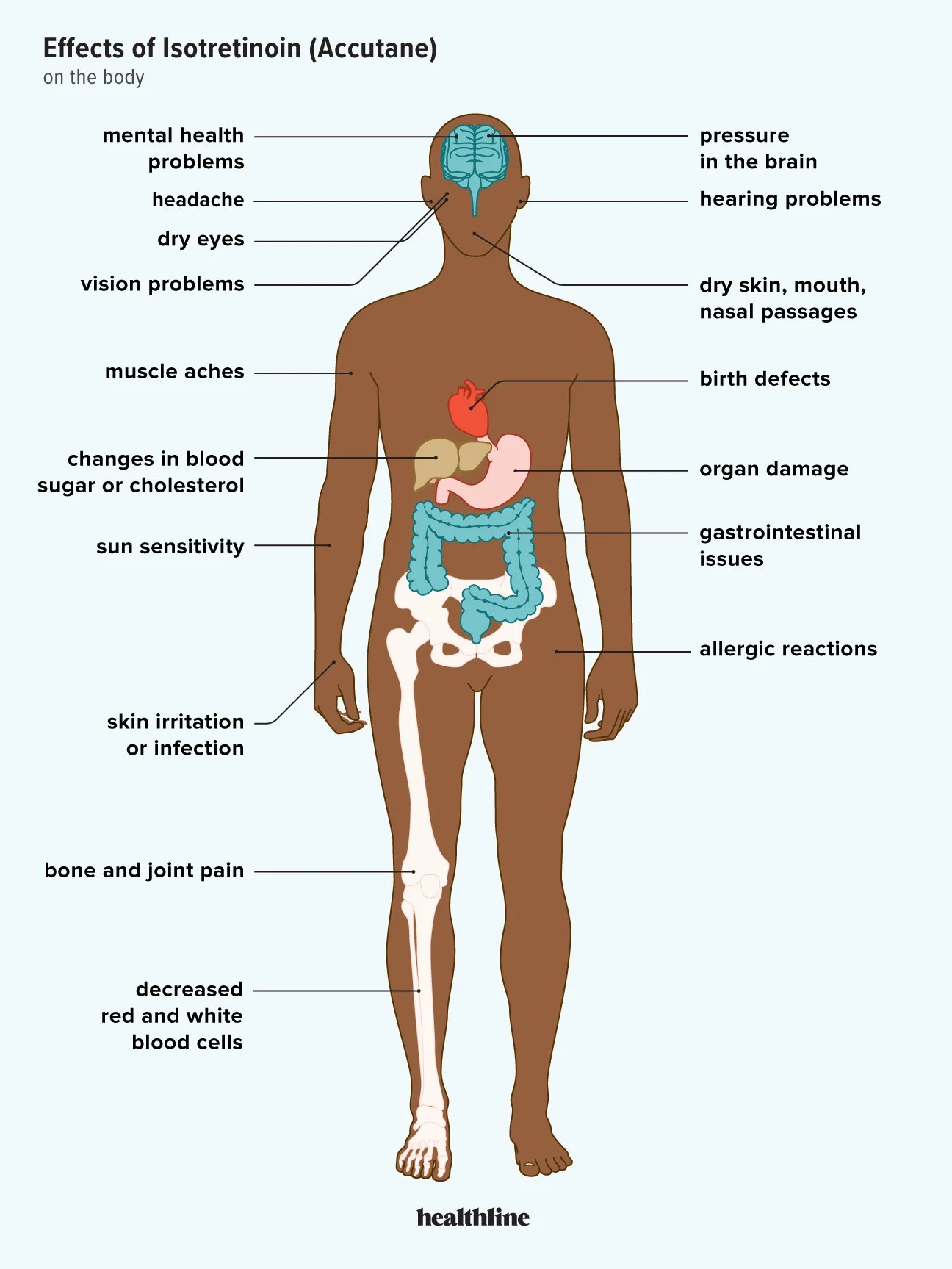
Accutane, a medication widely known for treating severe acne, has raised concerns regarding its potential link to long-term depression. Reports highlight that some individuals may experience despondency after completing their treatment. Recognizing these risks is critical if you’re considering Accutane as a treatment option.
Research indicates that while the majority of users do not experience lasting psychological effects, a subset reports increased feelings of sadness or anxiety. It’s advisable to monitor any changes in mood closely during and after treatment. Keeping an open line of communication with your healthcare provider can help address any emerging symptoms early on.
Building a support system is also beneficial. Engage with friends, family, or support groups to share your experiences. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, incorporating exercise and mindfulness practices into your routine, can further alleviate anxiety and promote overall well-being.
If you encounter persistent symptoms of depression, seek professional help. A mental health specialist can provide resources and strategies tailored to your needs, ensuring you receive comprehensive care during and after your Accutane experience.
- Accutane Long Term Depression: Understanding the Connection
- What is Accutane and Its Purpose in Acne Treatment?
- Mechanism of Action
- Duration and Outcomes
- Exploring the Chemical Composition of Accutane
- Clinical Evidence Linking Accutane and Depression
- Longitudinal Studies and Findings
- Clinical Recommendations
- Identifying Symptoms of Depression Post-Accutane Treatment
- Key Symptoms to Watch For
- When to Seek Help
- Psychological Mechanisms Behind Accutane-Induced Depression
- Long-Term Effects of Accutane on Mental Health
- Psychological Impact
- Recommendations for Users
- Strategies for Managing Depression After Accutane
- Therapeutic Approaches
- Nurturing Lifestyle Changes
- Consulting Healthcare Providers: Best Practices for Patients
- Be Open and Honest
- Prepare for Appointments
Accutane Long Term Depression: Understanding the Connection
Research indicates a potential link between Accutane (isotretinoin) and long-term depression in some individuals. Users of Accutane should monitor their mental health closely during and after treatment.
Accutane affects serotonin levels, which play a crucial role in mood regulation. Changes in serotonin can contribute to feelings of sadness or emotional instability. Studies have shown that a small percentage of patients report mood swings or depressive symptoms post-treatment.
If you experience mood changes, discuss them with a healthcare professional. A mental health evaluation can help identify any underlying issues and provide appropriate interventions. Therapy or support groups may assist in addressing emotional challenges.
Continuing self-care can also be beneficial. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and sufficient sleep support mental well-being. Engaging in activities that you enjoy can create a positive impact on mood.
For those with a history of depression, it’s essential to inform the prescribing physician before starting Accutane. They can help weigh the benefits against the risks and develop a monitoring plan during treatment.
Staying informed about the potential side effects of Accutane, including mental health risks, empowers you to take proactive steps for your well-being. Open communication with healthcare providers fosters a supportive treatment experience.
What is Accutane and Its Purpose in Acne Treatment?
Accutane, known generically as isotretinoin, is a potent medication specifically designed to treat severe acne that hasn’t responded to other treatments. It works by significantly reducing oil production in the skin, which helps prevent the formation of acne lesions. Patients typically receive Accutane under the supervision of a dermatologist to manage dosages and monitor potential side effects.
Mechanism of Action
This medication targets the sebaceous glands, decreasing their size and output. By minimizing skin oil, Accutane reduces acne-causing bacteria and inflammation. Additionally, it promotes cell turnover, helping to clear existing breakouts and preventing new ones from forming.
Duration and Outcomes
Accutane treatment usually lasts 4 to 6 months, with significant improvements often observed within weeks. Many patients achieve long-term remission from acne, making this drug a pivotal option in acne management. Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to assess progress and side effects, ensuring a safe treatment experience.
Exploring the Chemical Composition of Accutane
Accutane, known chemically as isotretinoin, is a retinoid derived from vitamin A. Its molecular formula is C20H28O2, consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The compound features a cyclohexene ring that contributes to its bioactivity, along with a conjugated double bond system that enhances its potency in targeting skin cell regulation.
Isotretinoin acts primarily by reducing sebum production, preventing clogged pores, and promoting cell turnover. This unique mechanism helps in effectively treating severe acne. It binds to retinoic acid receptors (RARs), influencing gene expression related to skin cellular functions.
Understanding its solubility is crucial. Isotretinoin is lipophilic, readily dissolving in fats and oils, which aids in its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. This characteristic warrants careful consideration of accompanying medications and dietary recommendations to optimize its efficacy.
Safety monitoring is vital due to Accutane’s potential side effects. Regular blood tests can track liver enzyme levels and lipid profiles. Awareness of isotretinoin’s interaction with other medications, especially those affecting liver metabolism, ensures a safer treatment approach.
Research indicates that isotretinoin may impact mental health over prolonged use, prompting further investigation into its long-term effects. Staying informed about these factors can aid clinicians in providing balanced care while managing treatment expectations for patients.
In summary, the chemical composition of Accutane plays a significant role in its effectiveness and safety in acne treatment. Awareness of its properties and potential ramifications helps in making informed decisions in clinical practices.
Clinical Evidence Linking Accutane and Depression
Research indicates a potential association between Accutane (isotretinoin) and depressive symptoms. A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology found a higher incidence of depression among adolescents treated with Accutane compared to those who received other acne therapies. This study highlights that patients should be monitored for mood changes during treatment.
Longitudinal Studies and Findings
Recent longitudinal studies have suggested a link between isotretinoin and increased risk of depression. For instance, a cohort study tracked over 1,000 patients and reported that 10% experienced depressive symptoms during treatment. The risk appeared to be higher in individuals with a history of mental health issues; thus, a thorough psychiatric evaluation is recommended before initiating treatment with Accutane.
Clinical Recommendations
Healthcare providers should conduct regular mental health assessments for patients undergoing Accutane therapy. Encourage open discussions about mood changes or depressive symptoms during follow-up appointments. For those with a history of depression, consider alternative treatments or a referral to a mental health specialist before starting isotretinoin.
Be vigilant about the signs of depression and educate patients about the importance of communicating any mental health concerns throughout their treatment journey.
Identifying Symptoms of Depression Post-Accutane Treatment
Monitor for changes in mood or behavior for signs of depression after completing Accutane treatment. Look for specific symptoms that may impact daily life.
Key Symptoms to Watch For
- Persistent sadness or low mood
- Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities
- Increased fatigue or low energy levels
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt
- Social withdrawal or isolation
- Thoughts of self-harm or suicide
When to Seek Help
Contact a healthcare professional if you experience several of these symptoms consistently for more than two weeks. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes.
Consider discussing your concerns with a trusted friend or family member for support. Keeping a journal of your feelings may also help both you and your healthcare provider understand your situation better.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind Accutane-Induced Depression
Research indicates that Accutane may alter neurotransmitter levels, particularly serotonin and dopamine, which are vital in mood regulation. Fluctuations in these chemicals can contribute to feelings of sadness and anxiety, leading to depression in some individuals.
Inflammation also plays a role. Accutane, by reducing sebaceous gland activity, might inadvertently increase inflammatory markers in the body. This elevated inflammation can affect brain function and contribute to mood disorders.
Additionally, the link between skin conditions and mental health cannot be overlooked. Patients undergoing Accutane treatment often struggle with acne-related social stigma and self-esteem issues. These psychological stressors can exacerbate feelings of isolation and sadness, adding to the drug’s potential depressive effects.
Monitoring mental health closely during treatment is essential. Health care providers should routinely assess patients for mood changes and provide appropriate support or interventions. Engaging with a therapist or counselor can also be beneficial, helping to address underlying issues stemming from both treatment and acne itself.
Open conversations about the risks and benefits of Accutane can equip individuals with the necessary tools to manage their mental health proactively. Creating a supportive environment among family and friends fosters resilience, helping those affected by potential emotional challenges during treatment.
Long-Term Effects of Accutane on Mental Health
Regular monitoring of mental health is crucial for individuals who have taken Accutane. Research indicates a potential link between isotretinoin use and long-term depressive symptoms. Reports suggest that some patients experience persistent mood alterations months or even years post-treatment.
Psychological Impact
Clinical studies show varying rates of depression among Accutane users. A small percentage of individuals may develop feelings of sadness or anxiety, which could escalate into more severe mental health challenges. It is advisable for past users to maintain open lines of communication with healthcare providers about any psychological changes they face after treatment.
Recommendations for Users
Engaging in regular physical activity, adopting a balanced diet, and ensuring adequate sleep can mitigate some mental health risks associated with Accutane. Support groups for shared experiences and professional therapy sessions may also provide beneficial coping mechanisms for those experiencing emotional distress. Prioritizing mental well-being is as important as addressing physical symptoms in the long run.
Strategies for Managing Depression After Accutane
Engage in regular physical activity. Exercise releases endorphins that help enhance mood and relieve stress. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities such as walking, cycling, or yoga can be particularly beneficial.
Therapeutic Approaches
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) provides practical strategies to challenge negative thoughts and develop coping mechanisms. Seek a licensed therapist who specializes in CBT to guide you through tailored exercises that target depressive symptoms.
Consider group therapy. Sharing experiences with others who have faced similar challenges can offer support and reduce feelings of isolation. Look for local or online support groups focused on mental health after dermatological treatments.
Nurturing Lifestyle Changes
Prioritize a balanced diet rich in nutrients. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts, may support brain health. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to maintain overall well-being.
Establish a regular sleep routine. Aim to sleep and wake at the same times each day. Limit screen time before bed and create a relaxing evening ritual to improve sleep quality.
| Strategy | Details |
|---|---|
| Exercise | Engage in 30 minutes of physical activity daily. |
| Therapy | Explore Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and group sessions. |
| Nutrition | Focus on a balanced diet with omega-3s, fruits, and vegetables. |
| Sleep Hygiene | Maintain a consistent sleep schedule and limit screens before bed. |
Stay connected with friends and family. Open up about your feelings and experiences to cultivate understanding and support. Regular social interactions can significantly enhance emotional well-being.
Consider mindfulness practices such as meditation or deep breathing exercises. Periods of mindfulness help ground thoughts and ease anxiety, contributing to better emotional balance.
Consulting Healthcare Providers: Best Practices for Patients
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor mental health. Discuss any changes in mood or behavior during Accutane treatment. These regular assessments help identify any potential side effects early on.
Be Open and Honest
Share your complete medical history and any existing mental health conditions with your provider. Transparency allows for tailored treatment and better management of potential risks. Mention all medications and supplements you are taking to avoid harmful interactions.
Prepare for Appointments
- List your symptoms, noting their frequency and intensity.
- Prepare questions regarding the side effects of Accutane, particularly related to mood and mental health.
- Understand the timeline for starting and completing treatment, including how to handle any complications.
Ask for resources or referrals to mental health professionals if you feel anxious or depressed. A supportive network is important for managing any emotional challenges during treatment.
Always communicate any new symptoms or side effects experienced while on Accutane. This feedback helps providers adjust treatment plans promptly and effectively.
Educate yourself about the medication. Knowledge about Accutane can empower you to discuss your care intelligently and advocate for your well-being.
Maintain a journal to track your mood and thoughts. Share this information with your healthcare provider to facilitate specific discussions regarding mental health throughout the treatment process.