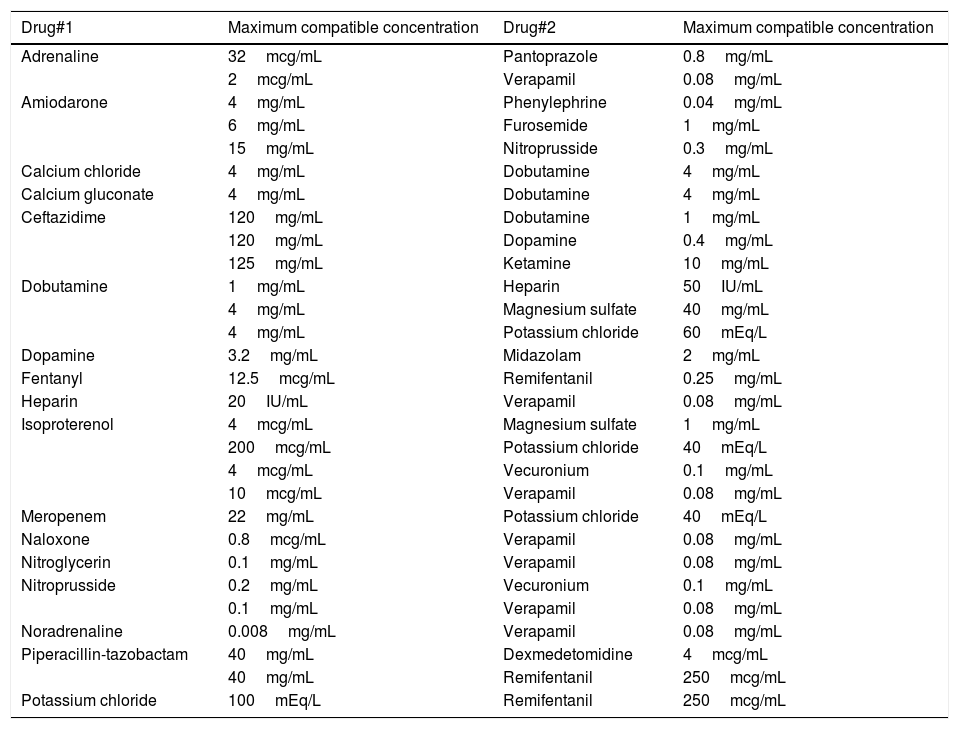
For optimal therapeutic outcomes, Zithromax (azithromycin) should only be administered intravenously in compatible formulations. It’s crucial to mix Zithromax with the appropriate diluent, such as 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose. Avoid mixing it with any solutions containing calcium, as this may lead to precipitation.
Before administering, always check for visible particles or discoloration in the solution. Ensure that the preparation adheres to the recommended concentration–typically between 1 mg/mL and 2 mg/mL–when diluted for intravenous administration. This promotes stability and minimizes the risk of adverse reactions.
Monitor infusion rates closely; the drug is administered over a period of 60 minutes to prevent irritation and enhance absorption. Avoid rapid bolus injection as it can trigger adverse side effects. Pay special attention to patients with known allergies or sensitivities to macrolides, ensuring their safety throughout the treatment.
Regularly consult updated compatibility guidelines and institutional protocols to guarantee adherence to current best practices when using Zithromax IV. Staying informed helps healthcare professionals provide the safest and most effective treatment for their patients.
- Zithromax IV Compatibility
- Compatible IV Solutions
- Incompatibilities
- Understanding Zithromax IV and Its Formulations
- Common Intravenous Solutions Compatible with Zithromax
- Precautions for Mixing Zithromax IV with Other Medications
- Storage and Handling Guidelines for Zithromax IV Solutions
- Clinical Implications of Zithromax IV Compatibility in Patient Care
Zithromax IV Compatibility
Zithromax IV (azithromycin) exhibits compatibility with various intravenous solutions but should not be mixed directly with other medications in IV solutions, as this may affect its effectiveness or stability.
Compatible IV Solutions
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection
- 5% Dextrose Injection
- Dextrose and Sodium Chloride Injection
When preparing Zithromax IV for administration, ensure the solution is clear and free of particles. Always inspect the vial for any discoloration before use.
Incompatibilities
- Do not combine with other antibiotics or medications in the same IV line without proper flushing.
- Avoid mixing with calcium-containing solutions to prevent precipitation.
Infusion of Zithromax IV should occur over a 60-minute period to reduce potential side effects. Closely monitor patients for any adverse reactions during and after administration. Maintain proper hygiene by using aseptic techniques throughout the process.
Consult with a pharmacist or healthcare provider for specific guidance tailored to individual patient needs or local protocols.
Understanding Zithromax IV and Its Formulations
Zithromax IV, or azithromycin for intravenous use, serves as a valuable treatment option for various bacterial infections, especially when oral administration is impractical. This formulation is particularly effective against respiratory tract, skin, and soft tissue infections, often utilized in hospital settings.
The IV formulation is designed for rapid absorption and can ensure higher plasma concentrations than oral counterparts. This attribute makes it suitable for patients with severe infections requiring immediate pharmacological intervention. Zithromax IV is typically administered as a slow intravenous infusion, which maximizes its therapeutic effects while minimizing potential side effects.
Zithromax comes in different concentrations, usually 500 mg or 1 g per vial. It’s crucial to reconstitute the drug appropriately before administration to maintain its stability and effectiveness. Mixing with compatible IV solutions, such as saline or dextrose, helps ensure a safe and effective infusion. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific instructions regarding preparation and compatibility.
Healthcare professionals must monitor patients for any adverse reactions during the infusion process. Common responses include nausea, diarrhea, or potential allergic reactions, although severe complications are rare. Close observation ensures any issues are addressed promptly, maintaining patient safety during treatment.
When considering Zithromax IV, evaluate the patient’s health status and infection severity. Discuss with the medical team to determine if this formulation aligns well with the treatment plan. Understanding the appropriate use of Zithromax IV can lead to successful outcomes in managing bacterial infections effectively.
Common Intravenous Solutions Compatible with Zithromax
Mix Zithromax with either Normal Saline or 5% Dextrose in Water (D5W) for safe intravenous administration. These solutions maintain compatibility and help ensure drug stability during infusion.
Normal Saline offers isotonic hydration and can also aid in dilution, making it a preferred choice. D5W provides a source of carbohydrates, which can be beneficial for patients requiring caloric support.
Avoid using Zithromax with solutions containing calcium as this may lead to precipitation. Solutions such as Lactated Ringer’s or any calcium-containing IV fluids should not be mixed. Always check specific compatibility charts or guidelines before proceeding with administration.
Consult with a pharmacist or healthcare provider for additional recommendations and ensure patient safety throughout the treatment process. Proper monitoring during the infusion is also advisable to identify any adverse reactions promptly.
Precautions for Mixing Zithromax IV with Other Medications
Do not mix Zithromax IV with any solution that contains calcium, including Ringer’s solution. This combination can lead to precipitation and serious complications. Use only compatible diluents, such as 0.9% Sodium Chloride or 5% Dextrose in Water for reconstitution.
Be cautious with concurrent administration of other antibiotics. Certain antibiotics may enhance or inhibit the effects of Zithromax, impacting the overall treatment outcome. Consult a healthcare provider to evaluate potential interactions before mixing.
Monitor patients for signs of adverse reactions when combining Zithromax with other medications, especially those affecting the heart, such as antiarrhythmics. QT interval prolongation may occur, leading to arrhythmias. Regular ECG checks can help ensure patient safety.
Review the patient’s complete medication history. Some medications known to interact with Zithromax include warfarin and certain antiepileptics. Adjust dosages as necessary under guidance from a healthcare professional.
Administer Zithromax IV slowly to reduce the risk of infusion-related reactions. Infusing too quickly may cause discomfort or thrombophlebitis. Observing the patient during administration helps identify any immediate reactions.
Always adhere to recommended dosages and schedules. Overdosing can increase the risk of side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Proper dosing improves treatment efficacy without compromising patient health.
Storage and Handling Guidelines for Zithromax IV Solutions
Store Zithromax IV solutions at controlled room temperature, ideally between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Avoid exposure to excessive heat and light. Keep the solution in its original packaging until ready for use to protect it from light.
Inspect the solution before administration. Do not use Zithromax IV if you notice any discoloration or visible particles. Ensure the solution is clear and free from any impurities.
After reconstitution, Zithromax IV solutions can be stored at room temperature for up to 24 hours. If refrigeration is necessary, maintain a temperature range of 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and use within 48 hours. Always label reconstituted solutions with the date and time of preparation.
Discard any unused portions of the solution after 24 hours post-reconstitution or if the storage conditions exceed the recommended limits. Follow institutional policies for the disposal of medical waste.
Minimize the risk of contamination during handling. Use aseptic techniques and avoid touching the solution or equipment that comes into contact with it. Ensure that any syringes or IV lines used are sterile.
Consult the specific product guidelines for any additional instructions or variations. Adhering to these storage and handling recommendations ensures the integrity of Zithromax IV solutions and maximizes patient safety.
Clinical Implications of Zithromax IV Compatibility in Patient Care
Zithromax (azithromycin) IV compatibility significantly impacts patient safety and treatment efficacy. Clinicians should refer to established compatibility charts when combining Zithromax with other intravenous medications. This reduces the risk of precipitate formation, which could compromise drug delivery.
Administering Zithromax alongside incompatible medications can lead to various complications, including infusion reactions and decreased therapeutic effects. Therefore, healthcare professionals must closely monitor the IV setup.
| Medication | Compatibility with Zithromax | Clinical Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Ceftriaxone | Incompatible | Avoid co-administration; use separate lines. |
| Vancomycin | Compatible | Administer via the same line if properly flushed. |
| Metronidazole | Compatible | Can be infused together; ensure proper dilution. |
Monitoring patient responses during infusion also remains critical. Observing for any signs of allergic reactions or adverse effects leads to prompt interventions, enhancing patient care quality. Understanding the compatibility of Zithromax IV aids in optimizing treatment regimens and improving patient outcomes.