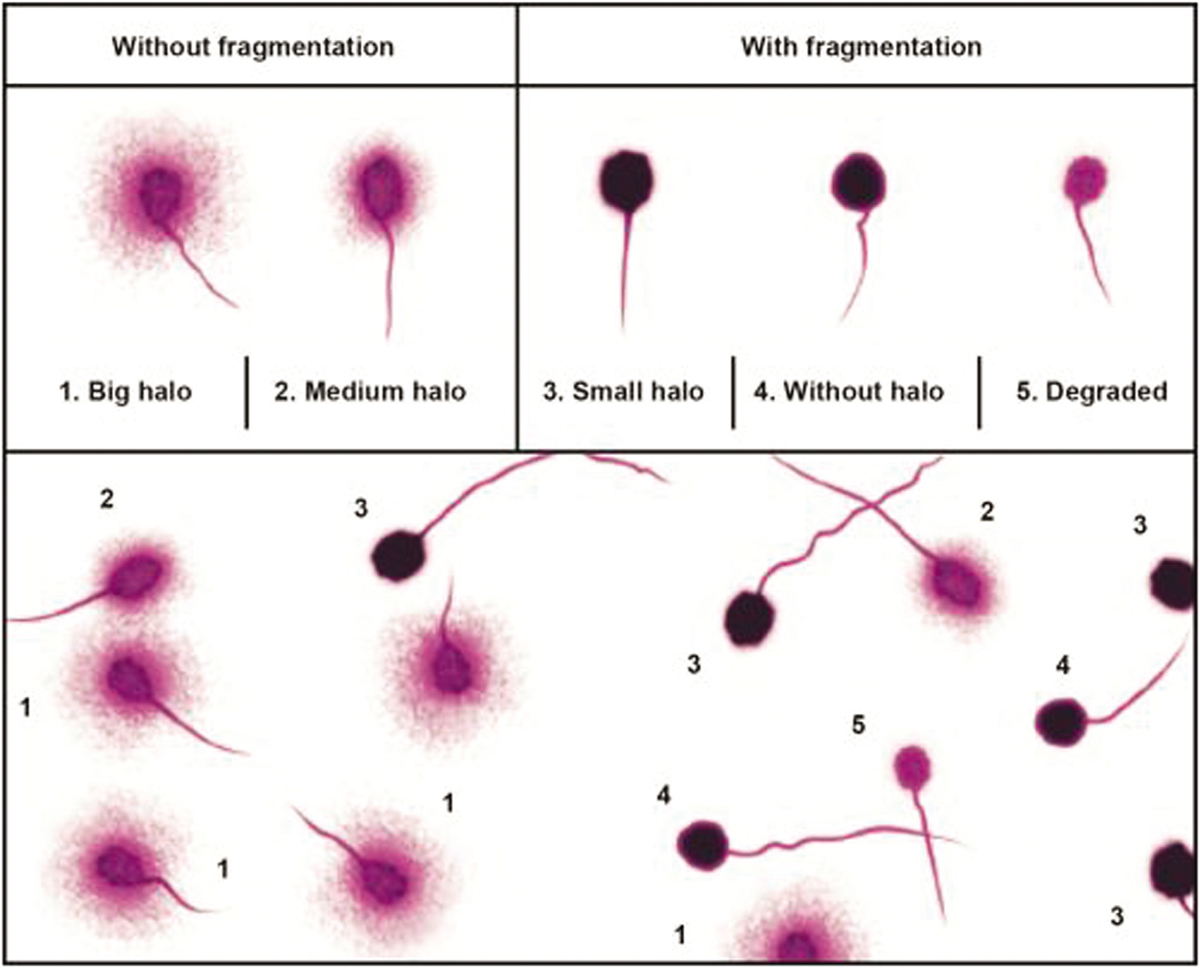
Consider discussing Propecia with your doctor if you are experiencing male infertility. Propecia, which contains finasteride, primarily utilized to treat hair loss, has raised concerns regarding its potential impact on fertility. Research indicates that some men may experience altered sperm parameters while undergoing treatment.
Several studies point to a correlation between finasteride use and reduced sperm count and motility. One study showed a decrease in semen quality in men who took Propecia, suggesting that while it addresses hair loss, it might simultaneously affect reproductive health. Be proactive and monitor any changes in your body while on this medication.
If you’re planning to conceive or already facing challenges with fertility, consult your healthcare provider about alternatives to Propecia. They can guide you towards safe options that maintain hair health without compromising your fertility. Taking control of your reproductive health starts with informed decisions based on your specific circumstances.
- Propecia and Male Infertility
- Understanding Propecia: Mechanism of Action
- Implications for Male Infertility
- Effects of Propecia on Male Hormones and Sperm Production
- Impact on Testosterone Levels
- Sperm Production and Quality
- Research Findings: Propecia’s Impact on Fertility Rates
- Case Studies: Male Infertility Associated with Propecia Use
- Alternatives to Propecia for Hair Loss Without Fertility Risks
- Natural Supplements
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Propecia and Male Infertility
Research indicates a potential link between Propecia (finasteride) use and male infertility. Users should consult with healthcare professionals before making decisions regarding this medication.
Propecia works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is essential for certain reproductive functions, and its reduction can lead to hormonal imbalances, which may affect fertility.
Studies have shown that men taking Propecia experienced altered sperm parameters, including decreased sperm count and motility. While some individuals report reversibility of these effects after discontinuing the medication, not all users see recovery.
Here’s a summary of findings related to Propecia and male fertility:
| Study | Findings |
|---|---|
| Study 1 | Reduced sperm count in men using Propecia for over six months. |
| Study 2 | Improved sperm parameters after discontinuation; recovery varied by individual. |
| Study 3 | No significant long-term infertility effect in short-term users. |
Potential side effects include decreased libido and erectile dysfunction, further complicating fertility issues. Discussing these risks with a urologist or reproductive specialist is advisable for those considering or currently using Propecia and facing infertility concerns.
Consider alternative treatments or lifestyle modifications to address hair loss without affecting fertility, including topical solutions or lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring of hormonal levels may also provide insights into any changes related to medication.
Understanding Propecia: Mechanism of Action
Propecia, or finasteride, operates by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. This enzyme converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a more potent form of testosterone. By blocking this conversion, Propecia effectively lowers DHT levels in the scalp and other tissues.
Here’s how it works:
- Reduction of DHT: With less DHT present, the miniaturization of hair follicles slows down, helping to prevent hair loss.
- Restoration of Hair Growth: Some users experience regrowth of hair or increased density after prolonged use, as follicles may recover due to decreased DHT levels.
- Hormonal Balance: Lowering DHT can lead to changes in hormonal levels, affecting libido and possibly fertility in certain men.
Implications for Male Infertility
While Propecia is primarily prescribed for hair loss, alterations in hormonal balance can impact fertility. The reduced DHT might lead to lower sperm production and motility in some individuals. Men considering Propecia should discuss any potential fertility concerns with their healthcare provider, especially if they plan to conceive.
Research indicates that while some men may not experience fertility issues, others might find that the drug affects their reproductive health. Monitoring testosterone and related hormone levels during treatment can be beneficial for those concerned about infertility.
Ultimately, understanding how Propecia functions empowers users to make informed decisions regarding its use and any potential side effects related to fertility.
Effects of Propecia on Male Hormones and Sperm Production
Propecia, primarily used to treat male pattern baldness, affects male hormones significantly. It inhibits the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This reduction in DHT levels can lead to hormonal imbalances.
Impact on Testosterone Levels
Patients often experience changes in testosterone levels. While total testosterone might remain stable, free testosterone levels may increase due to the decreased conversion to DHT. This elevation in free testosterone can influence libido and overall sexual function.
Sperm Production and Quality
Propecia has been associated with decreased sperm production and quality in some users. Research indicates potential reductions in sperm concentration and motility, which can lead to challenges in conception. Monitoring sperm parameters is advisable for those considering starting this medication.
If you are concerned about fertility, consult a healthcare provider before initiating treatment with Propecia. They can assess risks and provide options to manage any adverse effects on hormone levels and reproductive health.
Research Findings: Propecia’s Impact on Fertility Rates
Recent studies indicate a link between Propecia use and alterations in male fertility rates. Men taking this medication for androgenetic alopecia may experience changes in sperm parameters.
- A study published in the “Journal of Urology” revealed that a group of men using Propecia exhibited a notable decrease in sperm concentration. Participants showed an average reduction of 25% over 12 months of usage.
- Research presented at the American Urological Association highlighted that men affected by Propecia had diminished motility rates in sperm samples. This reduction averaged around 15%, impacting the likelihood of successful conception.
- Another significant investigation found a correlation between Propecia use and hormonal changes. Specifically, a decrease in testosterone levels was observed, which may affect overall reproductive health.
For couples trying to conceive, it’s advisable to assess the use of Propecia. Consulting a healthcare professional can provide insights into alternative treatments for hair loss that might not influence fertility.
Continuous monitoring of additional research on Propecia and its implications for male reproductive health remains critical. Keeping informed ensures better decision-making regarding family planning and treatment options.
Case Studies: Male Infertility Associated with Propecia Use
A 35-year-old man reported decreased libido and difficulties conceiving after using Propecia for three years. His sperm analysis revealed a significant reduction in sperm count and motility. After discontinuing Propecia, his sperm parameters improved within six months, leading to successful conception.
Another case involved a 29-year-old patient who experienced infertility after being on Propecia for two years. Hormonal tests indicated altered testosterone levels, contributing to his infertility issues. Treatment focused on restoring hormonal balance, and after cessation of the medication, he achieved normal testosterone levels and fathered a child within eight months.
A 42-year-old man experienced erectile dysfunction alongside infertility. He attributed these problems to Propecia use. Subsequent evaluations showed low levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). After stopping the medication and undergoing hormonal treatment, the patient’s reproductive health improved, resulting in pregnancy after one year.
In yet another case, a couple sought help due to prolonged infertility. The male partner had been on Propecia for five years. Testing indicated oligospermia and decreased sperm viability. Two months post-discontinuation, follow-up analysis showed marked improvements, and the couple conceived shortly after.
These cases highlight the potential link between Propecia use and male infertility. Awareness and monitoring of reproductive health may help mitigate these risks for men considering or currently using the medication. Consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable for those facing fertility concerns while on Propecia.
Alternatives to Propecia for Hair Loss Without Fertility Risks
Consider using minoxidil, a topical solution that promotes hair growth without affecting testosterone levels. This product is available over-the-counter and is suitable for both men and women. Studies have shown that minoxidil stimulates hair follicles and can result in noticeable hair regrowth within a few months of consistent use.
Natural Supplements
Explore biotin and pumpkin seed oil. Biotin supports keratin production, which is vital for hair health. Pumpkin seed oil contains phytosterols that may inhibit DHT, a hormone linked to hair loss, without the side effects associated with synthetic medications. Regular supplementation can enhance hair thickness and overall appearance.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Consider low-level laser therapy devices designed for home use. This treatment uses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate hair follicles, improving circulation and promoting hair growth. Many users report positive results with consistent application, making it a non-invasive option free from hormonal side effects.
Incorporating a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids, can also support hair health. Foods like fish, nuts, and leafy greens can provide your body with the nutrients it needs to maintain hair vitality.
Consult a healthcare professional to tailor the best approach for your hair loss concerns while considering any potential impacts on fertility. This ensures that you’re making informed decisions that align with your health goals.