Clomid has proven to be a reliable and widely used medication in the treatment of infertility, but it can sometimes lead to delays in ovulation. If you’ve been taking Clomid and notice changes in your cycle, consider monitoring your body closely. Keeping track of basal body temperature and using ovulation predictor kits can provide insight into your ovulation patterns.
Consult your healthcare provider if you experience significant delays. They can conduct tests to rule out other underlying issues such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid dysfunction. Adjusting the dosage or duration of Clomid may help to restore normal ovulation timing.
Additionally, lifestyle factors can play a substantial role in ovulation. Maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and manage stress levels. These changes can enhance your overall reproductive health and may help mitigate any delays caused by Clomid.
Understanding your body’s signals is key. Keep a journal to note your cycle changes and any other symptoms alongside your Clomid regimen. This information can be invaluable for discussions with your doctor and for determining the next steps in your fertility journey.
- Ovulation Delayed by Clomid: Understanding the Implications
- Monitor Your Cycle
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider
- What is Clomid and How Does it Work?
- Mechanism of Action
- Usage and Considerations
- Identifying Symptoms of Delayed Ovulation on Clomid
- Basal Body Temperature
- Cervical Mucus Changes
- Common Reasons for Ovulation Delay While Taking Clomid
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Stress and Lifestyle Factors
- Testing and Monitoring Ovulation During Clomid Treatment
- Impact of Delayed Ovulation on Fertility Treatment Goals
- Effects on Timing and Coordination
- Impact on Patient Emotional Well-being
- Alternative Strategies When Clomid Delays Ovulation
- Dietary Changes
- Herbal Supplements
- Consulting Healthcare Providers: When to Seek Help
- Signs to Monitor
- Questions to Ask
Ovulation Delayed by Clomid: Understanding the Implications
If you experience delayed ovulation while taking Clomid, monitor your cycle closely. Clomid works by stimulating ovary function, but individual responses can vary significantly. Some women may notice a shift in their ovulation timeline, which can be frustrating during the fertility journey.
Monitor Your Cycle
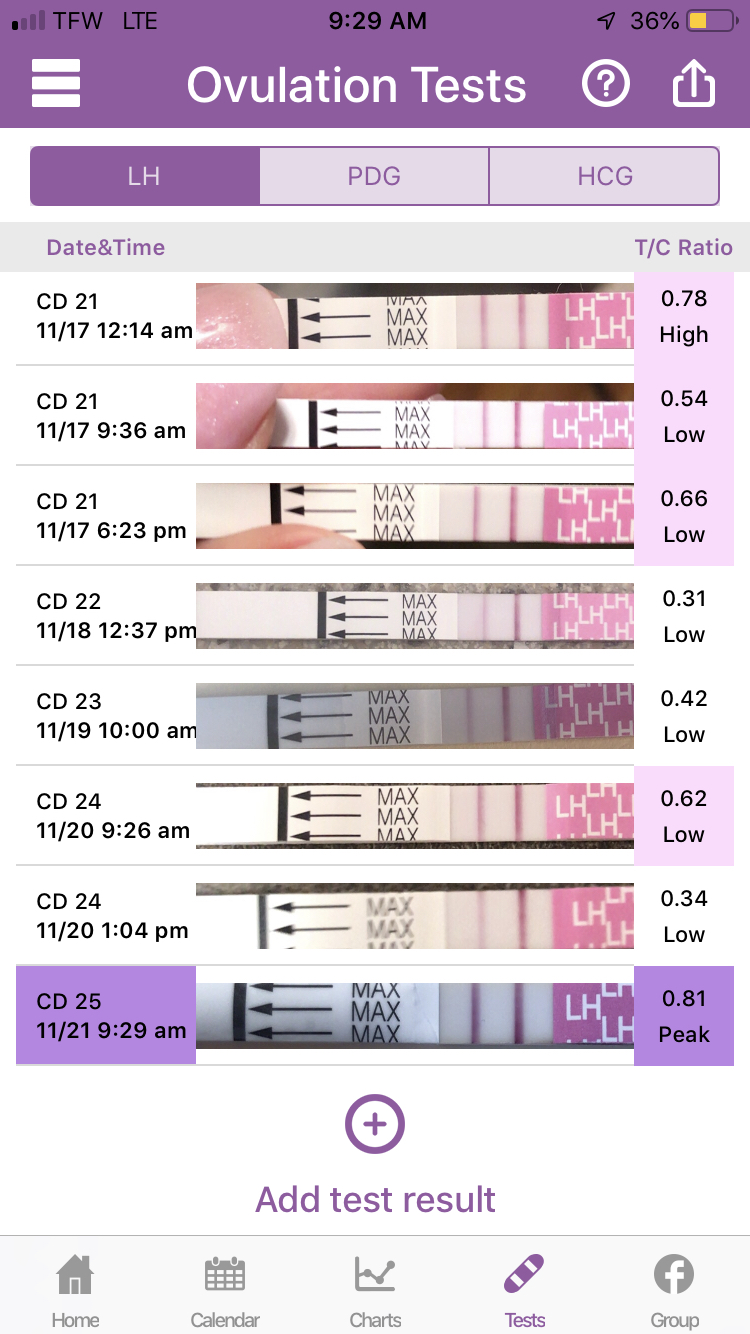
Keep track of ovulation signs, such as changes in cervical mucus or body temperature. Using ovulation predictor kits can provide clarity. This tracking informs you of your unique cycle adjustments and helps in planning intercourse effectively.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Discuss any delays with your healthcare provider. They might adjust your dosage or recommend additional testing. Understanding your body’s response ensures you receive the most suitable care tailored to your situation.
What is Clomid and How Does it Work?
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, is a commonly prescribed medication for women experiencing ovulatory disorders. It functions as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). By binding to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, Clomid effectively tricks the brain into believing that estrogen levels are low. This triggers the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), leading to increased secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland.
Mechanism of Action
The surge in FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, while the rise in LH triggers ovulation. Clomid typically initiates ovulation within 5 to 10 days after the last dose, which is usually taken for five days early in the menstrual cycle. Monitoring through ultrasounds or blood tests helps assess the development of follicles and determine ovulation timing.
Usage and Considerations
Doctors often recommend Clomid for women who do not ovulate regularly or for those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Treatment cycles usually last up to three to six months. If Clomid fails to induce ovulation, further evaluation or alternative treatments may be necessary. Side effects can include mood swings, hot flashes, and in some cases, visual disturbances. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider ensure optimal results and safety throughout the treatment process.
Identifying Symptoms of Delayed Ovulation on Clomid
Monitor your body for specific symptoms to identify delayed ovulation while taking Clomid. Common signs include changes in basal body temperature, inconsistent menstrual cycle patterns, and variations in cervical mucus. Tracking these indicators can help in understanding your cycle.
Basal Body Temperature
Note any fluctuations in basal body temperature (BBT). Typically, BBT rises after ovulation. A lack of an expected temperature increase may indicate a delay. Taking your temperature at the same time each morning can provide reliable data.
Cervical Mucus Changes
Observe the characteristics of cervical mucus. During ovulation, mucus often becomes clear, stretchy, and slippery–similar to raw egg whites. If this change does not occur, it might signal delayed ovulation. Regularly checking the mucus throughout your cycle aids in recognizing patterns.
If you notice your usual symptoms of impending ovulation are absent or irregular, consult your healthcare provider. They may suggest additional monitoring or adjustments to your Clomid dosage. Keeping a symptom diary can facilitate discussions with your doctor about your experience and concerns.
Common Reasons for Ovulation Delay While Taking Clomid
Several factors can lead to ovulation delay during Clomid treatment. One frequent reason is inadequate dosage. If the dosage isn’t sufficient to stimulate the ovaries, ovulation may not occur. Consult with your healthcare provider about adjusting the dose.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances play a significant role. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can interfere with hormone production, leading to delayed ovulation. Regular monitoring of hormone levels through blood tests can help identify such issues.
Stress and Lifestyle Factors
Stress affects ovulation by disrupting hormonal signals in the body. High-stress levels can lead to irregular cycles or delayed ovulation. Incorporating stress management techniques like yoga or meditation may prove beneficial. Additionally, lifestyle factors, such as excessive exercise or poor diet, can also hinder ovulation. Maintaining a balanced diet and a moderate exercise routine aids in overall reproductive health.
Lastly, certain medications may interact with Clomid and alter its effectiveness. Always inform your doctor about any other medications you are taking to ensure compatibility. Regular follow-ups will help you stay on track and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Testing and Monitoring Ovulation During Clomid Treatment
Track your ovulation closely during Clomid treatment to assess its effectiveness. Begin by using ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) around the expected ovulation window. These kits detect the surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) that occurs just before ovulation.
Combine OPKs with regular basal body temperature (BBT) charting. Measure your temperature first thing in the morning before getting out of bed. An increase in BBT typically indicates that ovulation has occurred. Keep a detailed chart to spot patterns over multiple cycles.
Additionally, consider ultrasound monitoring. Your healthcare provider may schedule ultrasounds during the cycle to evaluate the development of ovarian follicles. This can provide valuable insights into how well Clomid is working and whether ovulation is occurring properly.
Some clinicians may also recommend blood tests to measure progesterone levels about a week after the expected ovulation date. Elevated progesterone confirms that ovulation has occurred. Make sure to discuss which monitoring methods suit your circumstances best.
| Method | Purpose | Timing |
|---|---|---|
| Ovulation Predictor Kit (OPK) | Detect LH surge | Days leading up to expected ovulation |
| Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Charting | Confirm ovulation | Daily, throughout the cycle |
| Ultrasound Monitoring | Monitor follicle development | As directed by healthcare provider |
| Progesterone Level Testing | Confirm ovulation | About one week post-ovulation |
Consistent monitoring enhances your chances of success with Clomid. Stay in close communication with your healthcare provider to optimize your treatment plan based on these findings.
Impact of Delayed Ovulation on Fertility Treatment Goals
Delayed ovulation can significantly influence the success of fertility treatments. Understanding the specific effects allows for targeted strategies to enhance treatment outcomes.
Effects on Timing and Coordination
Delayed ovulation affects the synchronization of various treatment phases. This can lead to:
- Increased Monitoring: Regular ultrasound examinations may become necessary to determine the ovulation window.
- Modified Medication Dosage: Adjustments in Clomid or other fertility medications may be required to stimulate ovulation effectively.
- Altered Insemination or Transfer Timing: Timelines for artificial insemination or embryo transfer may shift, potentially impacting the chances of conception.
Impact on Patient Emotional Well-being
Delayed ovulation can also influence emotional aspects of treatment:
- Heightened Anxiety: Uncertainty about ovulation may increase stress levels among patients.
- Need for Support: Patients may benefit from counseling or support groups to manage emotional challenges.
By addressing the implications of delayed ovulation within fertility treatment, patients and providers can implement strategies for improved outcomes and greater emotional resilience. Prioritizing communication and ongoing assessment leads to a more tailored approach for each individual.
Alternative Strategies When Clomid Delays Ovulation
Consider adding lifestyle modifications to enhance your chances of ovulation. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can significantly impact reproductive health. Aim for a healthy weight, as both underweight and overweight conditions can disrupt hormonal balance.
Dietary Changes
Incorporate nutrient-rich foods, focusing on:
- Fruits and vegetables: Aim for a variety of colors to maximize nutrient intake.
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat help maintain energy levels.
- Healthy fats: Include sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil for hormone support.
Stay hydrated and limit processed foods, sugars, and trans fats.
Herbal Supplements
Explore natural supplements that may offer support:
- Myo-Inositol: Linked to improved ovarian function and regular cycles.
- Vitex (Chaste Tree Berries): May help regulate menstrual cycles by impacting progesterone levels.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Support overall hormonal health and may improve egg quality.
Consult a healthcare provider before introducing any supplements to ensure they align with your needs.
Monitor your menstrual cycle closely. Utilize ovulation kits or track basal body temperature to identify your peak fertile days. This can help you time intercourse effectively.
If Clomid continues to cause ovulation delays, engage in discussions with your healthcare provider about alternative medications or treatment options, such as Letrozole or injectable hormones. Tailoring your approach can lead to better outcomes.
Consulting Healthcare Providers: When to Seek Help
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience an unexpected delay in ovulation while taking Clomid. A delay beyond the expected ovulation window may indicate a need for further evaluation or adjustments in your treatment plan.
Signs to Monitor
Monitor for symptoms such as inconsistent menstrual cycles, excessive weight gain or loss, and unusual mood changes. These signs can provide important clues to your healthcare provider about hormonal imbalances or other underlying conditions.
Questions to Ask
Prepare questions for your healthcare provider about the duration of Clomid treatment, potential side effects, and alternative options if ovulation continues to be delayed. Understanding your treatment path is key to navigating fertility challenges effectively.