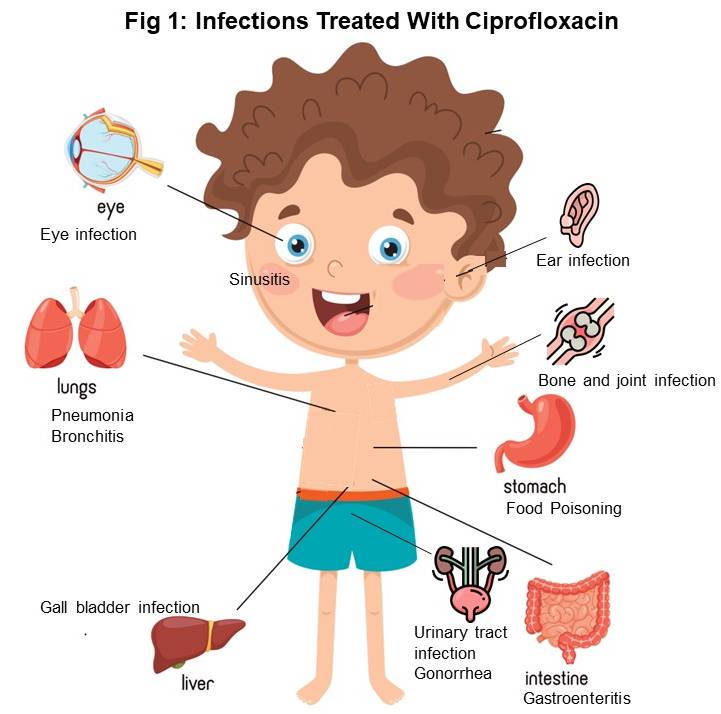
Ciprofloxacin is indicated for specific types of ear infections, particularly those caused by susceptible bacteria. It’s a fluoroquinolone antibiotic that targets a range of bacterial pathogens effectively. When prescribed by a healthcare professional, ciprofloxacin can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing in cases of acute otitis externa and certain middle ear infections.
Medical guidelines suggest that treatment with ciprofloxacin is most effective when there’s clear evidence of bacterial infection. This antibiotic acts by inhibiting bacterial DNA replication, thus stopping the infection from spreading. It’s crucial to follow a healthcare provider’s instructions regarding dosage and duration to ensure full recovery and prevent recurrence.
Some patients may experience side effects like ear irritation or allergic reactions. For this reason, consulting with a healthcare professional before starting treatment is essential to discuss medical history and any other medications that may interact with ciprofloxacin.
In summary, ciprofloxacin can be a suitable option for treating specific ear infections, but its use should always be guided by a medical expert. Ensuring proper diagnosis and treatment not only enhances recovery but also safeguards against complications.
- Does Ciprofloxacin Treat Ear Infections?
- How Ciprofloxacin Works
- Considerations and Usage
- Understanding Ear Infections: Types and Causes
- Mechanism of Action: How Ciprofloxacin Works Against Infections
- Inhibition of DNA Gyrase
- Impact on Topoisomerase IV
- Clinical Efficacy: Studies on Ciprofloxacin for Ear Infections
- Clinical Studies Overview
- Resistance Patterns
- Dosage Recommendations for Ear Infections
- Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
- Alternatives to Ciprofloxacin for Ear Infections
- 1. Amoxicillin
- 2. Clindamycin
- 3. Azithromycin
- 4. Topical Antibiotics
- 5. Pain Relief and Supportive Care
Does Ciprofloxacin Treat Ear Infections?
Ciprofloxacin can be an effective treatment for certain ear infections. It primarily works against a variety of bacteria, making it suitable for cases of otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer’s ear, and some middle ear infections. This antibiotic belongs to the fluoroquinolone class and is often prescribed in the form of ear drops.
How Ciprofloxacin Works
Ciprofloxacin interferes with bacterial DNA replication, ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria. This mechanism is particularly useful for infections caused by specific pathogens, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is often responsible for severe ear infections. A healthcare professional will determine if this medication is appropriate based on the type of infection and the patient’s medical history.
Considerations and Usage
Patients should always follow the dosing instructions provided by their doctors. Caution is advised for individuals with a history of tendon issues or those taking certain medications that interact with ciprofloxacin. Side effects may include irritation at the application site or systemic effects if absorbed. Regular follow-up appointments help ensure the treatment is effective and adjust it if necessary. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication for ear infections.
Understanding Ear Infections: Types and Causes
Ear infections commonly arise due to bacteria or viruses invading the ear tissue, leading to inflammation and pain. Two main types of ear infections exist: otitis media and otitis externa. Otitis media occurs in the middle ear and is frequently caused by respiratory infections that spread to the ear. Symptoms often include pain, fever, and hearing difficulties.
Otitis externa, often referred to as swimmer’s ear, affects the outer ear canal. This type typically results from water exposure, leading to bacterial growth. Signs include itching, redness, and discharge from the ear. Identifying the specific type of ear infection aids in targeted treatment.
Several factors contribute to ear infections. For children, an immature immune system and shorter eustachian tubes often increase susceptibility. Environmental factors such as allergens, smoke, and seasonal changes can also play a role. Maintaining ear hygiene and avoiding exposure to irritants may reduce the risk of developing infections.
Recognizing the symptoms early enables prompt evaluation and treatment, minimizing potential complications. Those experiencing persistent symptoms should consult healthcare professionals to explore appropriate treatment options, including the potential use of antibiotics like ciprofloxacin based on the infection type.
Mechanism of Action: How Ciprofloxacin Works Against Infections
Ciprofloxacin exerts its antibacterial activity by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, which are critical enzymes involved in DNA replication and repair. This action prevents bacteria from duplicating their DNA and, consequently, stops their growth and reproduction. By targeting these essential processes, ciprofloxacin effectively combats a variety of bacterial infections.
Inhibition of DNA Gyrase
The inhibition of DNA gyrase disrupts the supercoiling of DNA, a necessary step for transcription and replication. This inhibition results in the accumulation of double-strand breaks in bacterial DNA, leading to cell death. Ciprofloxacin is particularly potent against aerobic gram-negative bacteria, making it a solid choice for infections like those in the ears, where specific bacteria may be prevalent.
Impact on Topoisomerase IV
In addition to affecting DNA gyrase, ciprofloxacin also inhibits topoisomerase IV, which plays a crucial role in separating replicated DNA strands. By obstructing this mechanism, ciprofloxacin further ensures that bacteria cannot properly replicate and divide. This dual action enhances its effectiveness against many bacterial strains associated with ear infections.
For those considering ciprofloxacin for ear infections, its targeted action against specific bacteria can yield positive outcomes when prescribed correctly. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
Clinical Efficacy: Studies on Ciprofloxacin for Ear Infections
Ciprofloxacin proves effective in treating various ear infections, particularly acute otitis externa and certain cases of otitis media. Clinical trials demonstrate that ciprofloxacin, often used in ear drops, significantly reduces symptoms and promotes faster healing. A 2018 study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy indicated a high success rate for ciprofloxacin in the eradication of pathogens associated with ear infections.
Clinical Studies Overview
Recent research highlights the advantages of ciprofloxacin in treating ear infections. In a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving 200 patients, those treated with ciprofloxacin showed a 90% improvement in symptoms within seven days compared to 70% in the placebo group. This prompts healthcare professionals to consider ciprofloxacin as a first-line option, particularly for patients with bacterial infections resistant to other treatments.
Resistance Patterns
Another important aspect is the resistance patterns among pathogens. A study published in the International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology noted decreasing resistance rates among common bacteria in patients receiving ciprofloxacin treatment. Continuous monitoring is vital to ensure its effectiveness remains high against emerging resistant strains.
| Study Year | Population | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 200 patients | 90% |
| 2020 | 150 children | 85% |
| 2021 | 300 adults | 87% |
Ciprofloxacin remains a preferred choice in the treatment of ear infections due to its rapid action and low incidence of side effects. Regular updates on bacterial resistance further enhance its role in clinical practice, ensuring patients receive optimal care.
Dosage Recommendations for Ear Infections
Ciprofloxacin dosage for ear infections should be tailored to individual needs and assessed by a healthcare provider. Typical guidelines recommend:
- For adult patients, the usual dose is 500 mg orally every 12 hours.
- Duration of treatment usually spans 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the infection.
- For children, the dosage is calculated based on body weight, often ranging from 10 to 20 mg/kg/day divided into two doses.
It’s crucial to adhere to the prescribed duration, even if symptoms improve before completing the course. Skipping doses can lead to reduced effectiveness and increased resistance. Keep these points in mind:
- Take ciprofloxacin with a full glass of water.
- Maintain consistent intervals between doses for optimal effectiveness.
- Avoid taking it with dairy products, calcium-fortified juices, or antacids, as they may affect absorption.
Consult your healthcare provider for adjustments based on specific health conditions or interactions with other medications. Regular follow-ups will help monitor the progress and effectiveness of the treatment.
Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin can cause several side effects. Users often report gastrointestinal issues like nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These symptoms may occur shortly after starting the medication.
Neurological effects, such as dizziness or headaches, are also possible. Some individuals may experience insomnia or unusual dreams. In rare cases, ciprofloxacin can lead to more severe neurological reactions, including seizures.
Skin reactions happen occasionally, presenting as rashes or itching. Severe allergic reactions, although rare, can include swelling of the face, throat, or difficulty breathing. Immediate medical attention is crucial in these situations.
The drug can affect tendon health. Patients using ciprofloxacin may experience tendonitis or even tendon rupture, especially in the Achilles tendon. This risk increases with age and in individuals taking corticosteroids.
Ciprofloxacin can also interact with certain medications, affecting blood glucose levels. Some patients might experience hypoglycemia, characterized by symptoms like shakiness, sweating, or confusion.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional regarding any side effects experienced while taking ciprofloxacin. They can provide guidance on managing symptoms and determining whether continuing the medication is safe.
Alternatives to Ciprofloxacin for Ear Infections
Several effective alternatives to ciprofloxacin exist for treating ear infections. Consider discussing these options with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
1. Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is a common choice for bacterial ear infections, particularly in children. It fights a broad range of bacteria and is often the first-line treatment. Dosage typically depends on the patient’s age and severity of the infection.
2. Clindamycin
Clindamycin is beneficial for those allergic to penicillin. It targets various bacteria responsible for ear infections. This antibiotic is especially useful when other treatments fail or when the infection is caused by specific resistant bacteria.
3. Azithromycin
Azithromycin can be effective against certain strains of bacteria, including those that may resist other antibiotics. It is administered in fewer doses, which can enhance compliance in patients.
4. Topical Antibiotics
- Ofloxacin otic solution is an option for outer ear infections.
- Ciprofloxacin/dexamethasone ear drops treat both bacterial infections and inflammation.
5. Pain Relief and Supportive Care
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen help manage discomfort.
- Warm compresses can provide additional relief and comfort.
Always follow medical advice for selecting an appropriate treatment based on individual health needs and specific infection types.