For those considering the vaginal use of Cytotec (misoprostol), it’s crucial to understand its applications and guidelines. Health professionals often recommend this method for various medical scenarios, including labor induction and management of miscarriage.
Administering Cytotec vaginally increases the effectiveness of the medication. Dosage typically varies based on the specific condition being treated, so you must consult with your healthcare provider for tailored instructions. Generally, the medication is inserted into the vagina as a tablet, allowing for localized action and better absorption.
Monitoring for side effects is key. Common reactions include cramping, diarrhea, and nausea. If you experience severe discomfort or other unusual symptoms, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider immediately. Being informed and prepared will help ensure a smoother experience.
In summary, when using Cytotec vaginally, adhering to medical guidance and being aware of potential side effects will enhance your overall experience and effectiveness of treatment.
- Cytotec Vaginally: An In-Depth Overview
- Understanding Cytotec and Its Medical Uses
- Indications for Vaginal Administration of Cytotec
- Potential Benefits of Using Cytotec Vaginally
- Recommended Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Possible Side Effects and Precautions
- Common Side Effects
- Serious Reactions
- Contraindications for Vaginal Use of Cytotec
- Pre-existing Conditions
- Pregnancy and Related Concerns
- Patient Testimonials and Experiences with Vaginal Cytotec
Cytotec Vaginally: An In-Depth Overview
Cytotec, containing the active ingredient misoprostol, is frequently administered vaginally to induce labor and manage postpartum hemorrhage. This route enhances the drug’s absorption and effectiveness. Administering Cytotec vaginally allows for localized action and minimizes systemic side effects.
When using Cytotec vaginally, healthcare providers typically recommend inserting a 25 microgram tablet into the posterior vaginal fornix. Dosing may vary based on individual patient needs and medical guidelines, with repeat doses usually given every 3 to 6 hours as necessary. Monitor the patient closely for contractions, fetal heart rate, and any potential side effects.
Side effects can include nausea, diarrhea, or uterine hyperstimulation. Educating patients on recognizing these symptoms ensures timely intervention. It is also essential to consider contraindications such as a history of uterine surgery or prior cesarean delivery, where the risk of rupture may increase.
Before administration, a thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history is critical. Checking for potential drug interactions and ensuring that the patient is a suitable candidate for vaginal delivery with Cytotec will contribute to favorable outcomes. Post-administration surveillance is necessary, particularly to assess uterine activity and fetal wellbeing.
The success of vaginal Cytotec often lies in the individualized approach to treatment. Communication between healthcare providers and patients, as well as adherence to established protocols, plays a key role in ensuring safety and efficacy throughout the process.
Understanding Cytotec and Its Medical Uses
Cytotec, or misoprostol, serves multiple medical purposes, primarily in gynecology and gastroenterology. It is a prostaglandin E1 analog, effective in various clinical settings. For instance, its use in the termination of early pregnancy is well-documented, where it acts to soften the cervix and induce uterine contractions. Doctors often recommend cytotec vaginally for this purpose due to its enhanced absorption and efficacy.
In addition to its role in abortion, Cytotec is frequently utilized in managing gastric ulcers. It protects the stomach lining by increasing mucus and bicarbonate secretion, thus mitigating the effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Clinicians may prescribe it alongside NSAIDs to prevent ulcer formation.
The table below summarizes the key medical uses and applications of Cytotec:
| Medical Use | Application | Administration Route |
|---|---|---|
| Induction of Abortion | Termination of early pregnancy | Vaginally or orally |
| Prevention of Gastric Ulcers | Protection against NSAID-induced damage | Orally |
| Cervical Ripening | Preparation for labor in pregnant women | Vaginally |
Precise dosing is crucial when using Cytotec for any purpose. Medical professionals tailor the dosage based on the specific condition being treated and patient history. Monitoring may be necessary to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Side effects, while not common, can include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and nausea. Patients should discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider before use. Understanding the implications of Cytotec usage empowers patients to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Indications for Vaginal Administration of Cytotec
Cytotec, or misoprostol, is commonly administered vaginally for various obstetric and gynecological indications. One prominent use is in the induction of labor, particularly for women who exhibit a medical need to initiate contractions due to conditions such as preeclampsia or gestational hypertension.
This route of administration allows for localized absorption, providing effective uterine stimulation. Vaginal Cytotec is also indicated for cervical ripening before surgical procedures, enhancing the likelihood of successful dilation. It reduces the risk of complications during labor and delivery.
Additionally, Cytotec is utilized to manage incomplete or missed miscarriages. Administering the drug vaginally in such cases promotes uterine contractions, facilitating the expulsion of retained tissue. This method provides a non-invasive option and can significantly reduce the need for surgical intervention.
Another indication includes treatment of postpartum hemorrhage. By promoting uterine contractions, vaginally administered Cytotec aids in reducing blood loss, ensuring a safer postpartum recovery.
Healthcare providers will evaluate specific patient circumstances to determine the appropriateness of vaginal administration of Cytotec, tailoring the approach to individual needs. Regular monitoring during administration allows for adjustments to enhance safety and effectiveness.
Potential Benefits of Using Cytotec Vaginally
Administering Cytotec vaginally offers several significant advantages. This method often leads to a more localized effect, enhancing the medication’s efficacy in inducing labor or managing miscarriage.
- Higher Bioavailability: Vaginal administration bypasses the gastrointestinal tract, allowing for better absorption and faster onset of action.
- Reduced Systemic Side Effects: Targeting the drug locally can minimize potential systemic side effects, making it a safer option for many patients.
- Convenient Dosage Administration: Vaginal tablets are easy to insert and can be self-administered, providing comfort and autonomy for patients.
- Effective Cervical Ripening: Cytotec can facilitate cervical ripening more efficiently when administered vaginally, potentially leading to improved labor outcomes.
- Fewer Doses Required: Vaginal use may result in the need for fewer doses compared to oral administration, aiding in patient compliance and comfort.
In addition to these benefits, using Cytotec vaginally allows healthcare providers to closely monitor the patient’s response, adjusting treatment plans as necessary. This approach can lead to better overall outcomes during labor induction or in the management of missed miscarriage.
Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the suitability of this administration route based on individual medical conditions and circumstances.
Recommended Dosage and Administration Guidelines
The standard recommended dose of Cytotec (misoprostol) for vaginal administration is typically 25 micrograms. This dosage can be repeated every 3 to 6 hours based on the clinical situation and physician’s judgment.
For induction of labor, a common protocol involves administering the initial dose, then assessing uterine activity and fetal status before any subsequent doses. Do not exceed a total of 200 micrograms in a 24-hour period unless otherwise directed by a healthcare professional.
Insert the tablet high into the posterior vaginal fornix. Ensure the patient is in a comfortable position to maximize absorption. Verify that the patient is monitored for adverse effects such as uterine hyperstimulation, which may require immediate medical attention.
Before considering the use of Cytotec, discuss any relevant medical history or potential contraindications with a healthcare provider. Tailor the administration plan to the patient’s individual needs, and adjust follow-up care accordingly.
For optimal outcomes, maintain a close watch on the patient’s symptoms and response to the treatment. Document all doses administered, timing, and any side effects experienced during the process.
Possible Side Effects and Precautions
Using Cytotec vaginally can lead to various side effects. Recognizing these effects helps ensure safety and informed use.
Common Side Effects
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headaches
- Dizziness
Serious Reactions
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe or prolonged abdominal pain
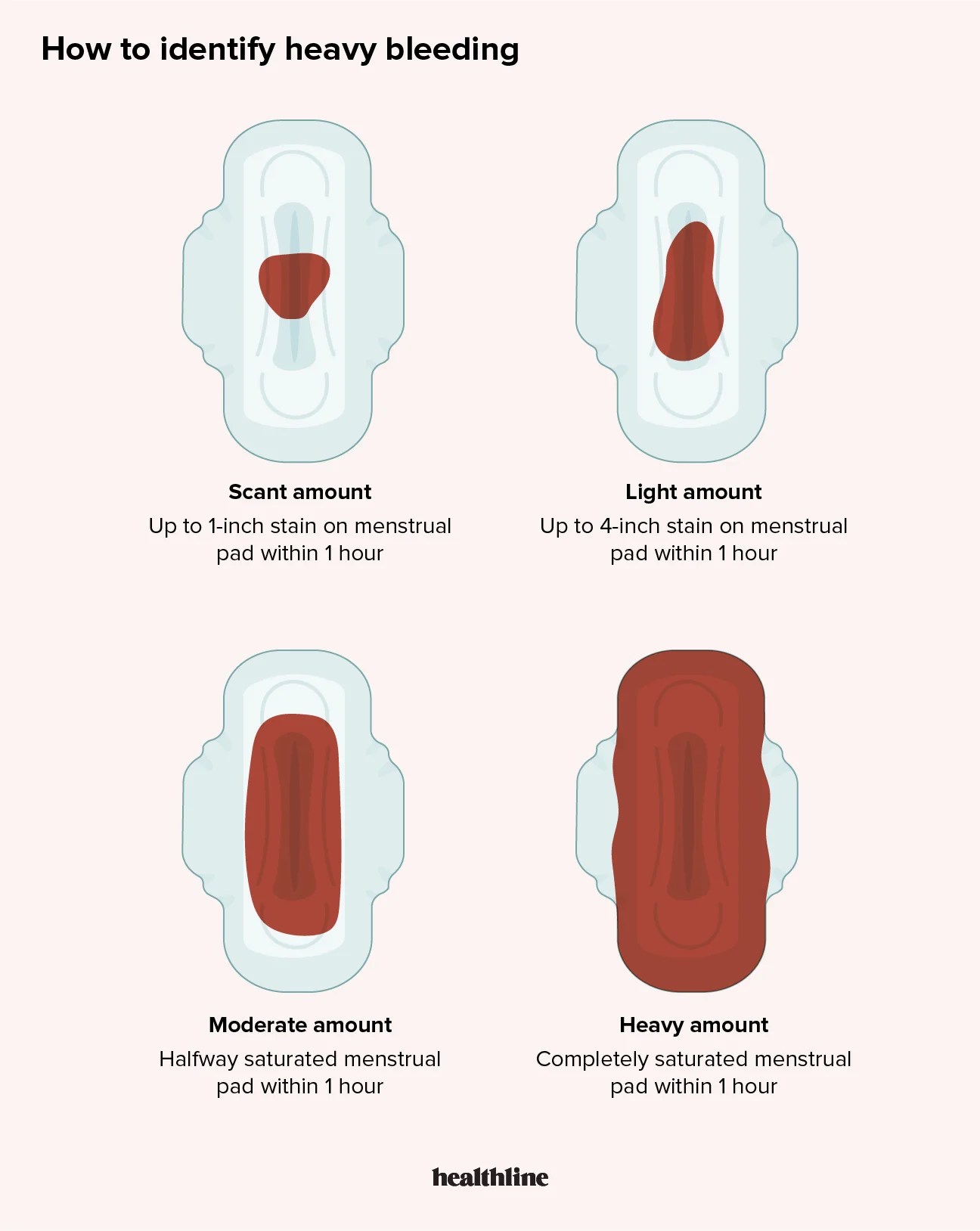
- Heavy bleeding or passing large clots
- Allergic reactions such as rash, itching, or swelling
- Signs of infection, including fever or chills
Consult your healthcare provider before use if you have:
- History of uterine surgery or cesarean delivery
- Known allergies to prostaglandins
- Severe cardiovascular or respiratory conditions
Consider potential drug interactions. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter supplements. Follow dosage instructions precisely and avoid self-adjusting without consultation.
Regular follow-up appointments ensure proper monitoring of effects and overall health while using Cytotec. Prioritize open communication with your healthcare provider to address any concerns or side effects promptly.
Contraindications for Vaginal Use of Cytotec
The vaginal use of Cytotec is not recommended in certain situations. First, avoid using Cytotec if you have a history of hypersensitivity to misoprostol or any of its components. Allergic reactions can lead to severe complications.
Pre-existing Conditions
Patients with a history of uterine scarring, such as from previous surgeries, should refrain from using Cytotec vaginally. This medication can cause uterine contractions, which may exacerbate existing conditions and lead to serious risks. Additionally, those with active pelvic infections should not use Cytotec, as it can worsen the infection or complicate treatment.
Pregnancy and Related Concerns
Vaginal administration of Cytotec is contraindicated for individuals who are not in the process of terminating a pregnancy or inducing labor. It can initiate uterine contractions prematurely, leading to potential harm for both mother and child. It’s essential to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice before considering this medication.
Patient Testimonials and Experiences with Vaginal Cytotec
Many patients report that using vaginal Cytotec has been a supportive experience during their medical procedures. One woman shared that after her doctor recommended it for induction, she felt more in control throughout the process. She appreciated that the medication acted quickly, enabling her to focus on her comfort rather than anxiety.
Another patient highlighted the minimal discomfort she experienced. She mentioned that the insertion was straightforward, and she was relieved that the effects began without prolonged waiting. Her doctor provided clear instructions, which helped ease her worries and contributed to a positive encounter.
A male partner reported that supporting his spouse through labor after the use of vaginal Cytotec made a significant difference. He noted that the communication between them flourished as they navigated the experience together, with the medication facilitating a smooth progression.
A woman who underwent an abortion shared that vaginal Cytotec helped manage her procedure with less pain than she anticipated. She felt empowered knowing her medical team was attentive and responsive, leading to a more manageable recovery period.
Overall, the feedback consistently emphasizes the importance of clear communication with healthcare providers. Many patients feel more at ease when they understand the process and can express their concerns openly, making their experiences with vaginal Cytotec generally positive.